C H A P T E R 12 IP Unicast Routing
203
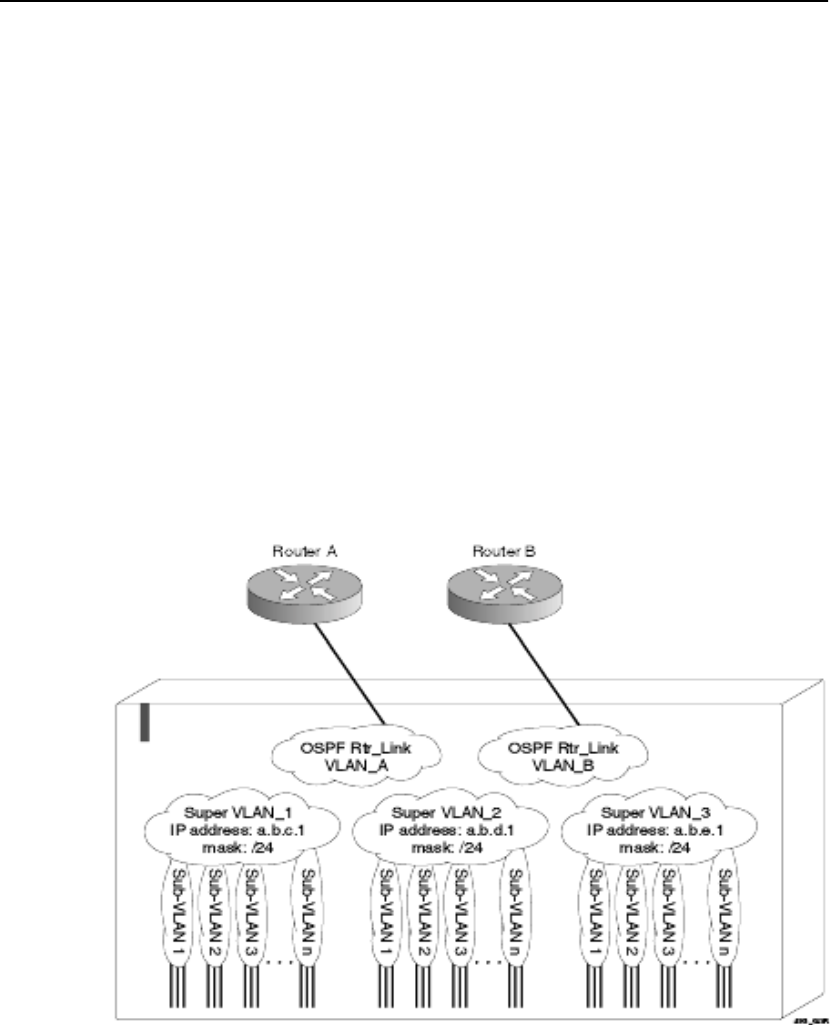
• The subVLANs use the IP address of the superVLAN as the
default router address.
• Groups of clients are then assigned to subVLANs that have no IP
address, but are members of the superVLAN.
• Clients can be informally allocated any valid IP addresses within
the subnet. Optionally, you can prevent communication between
subVLANs for isolation purposes so that subVLANs can be quite
small, but allow for growth without re-defining subnet
boundaries.
Without using VLAN aggregation, each VLAN has a default router
address, and you need to use large subnet masks. The result is more
unused IP address space.
Multiple secondary IP addresses can be assigned to the
superVLAN. These IP addresses are only used to respond to ICMP
ping packets to verify connectivity.
Figure 12.2 illustrates VLAN aggregation.
Figure 12.2: VLAN aggregation


















