www.national.com 152
CP3BT26
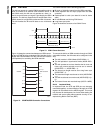
20.7.1 Audio Receive FIFO Register (ARFR)
The Audio Receive FIFO register shows the receive FIFO
location currently addressed by the Receive FIFO Read
Pointer (RRP). The receive FIFO receives 8-bit or 16-bit
data from the Audio Receive Shift Register (ARSR), when
the ARSR is full.
In 8-bit mode, only the lower byte of the ARFR is used, and
the upper byte contains undefined data. In 16-bit mode, a
16-bit word is copied from ARSR into the receive FIFO. The
CPU bus master has read-only access to the receive FIFO,
represented by the ARFR register. After reset, the receive
FIFO (ARFR) contains undefined data.
ARFL The Audio Receive FIFO Low Byte shows the
lower byte of the receive FIFO location cur-
rently addressed by the Receive FIFO Read
Pointer (RRP).
ARFH The Audio Receive FIFO High Byte shows the
upper byte of the receive FIFO location cur-
rently addressed by the Receive FIFO Read
Pointer (RRP). In 8-bit mode, ARFH contains
undefined data.
20.7.2 Audio Receive DMA Register n (ARDRn)
The ARDRn register contains the data received within slot
n, assigned for DMA support. In 8-bit mode, only the lower
8-bit portion of the ARDRn register is used, and the upper
byte contains undefined data. In 16-bit mode, a 16-bit word
is transferred from the Audio Receive Shift Register (ARSR)
into the ARDRn register. The CPU bus master, typically a
DMA controller, has read-only access to the receive DMA
registers. After reset, these registers are clear.
ARDL The Audio Receive DMA Low Byte field re-
ceives the lower byte of the audio data copied
from the ARSR.
ARDH In 16-bit mode, the Audio Receive DMA High
Byte field receives the upper byte of the audio
data word copied from ARSR. In 8-bit mode,
the ARDH register holds undefined data.
20.7.3 Audio Transmit FIFO Register (ATFR)
The ATFR register shows the transmit FIFO location cur-
rently addressed by the Transmit FIFO Write Pointer (TWP).
The Audio Transmit Shift Register (ATSR) receives 8-bit or
16-bit data from the transmit FIFO, when the ATSR is empty.
In 8-bit mode, only the lower 8-bit portion of the ATSR is
used, and the upper byte is ignored (not transferred into the
ATSR). In 16-bit mode, a 16-bit word is copied from the
transmit FIFO into the ATSR. The CPU bus master has
write-only access to the transmit FIFO, represented by the
ATFR register. After reset, the transmit FIFO (ATFR) con-
tains undefined data.
ATFL The Audio Transmit Low Byte field represents
the lower byte of the transmit FIFO location
currently addressed by the Transmit FIFO
Write Pointer (TWP).
ATFH In 16-bit mode, the Audio Transmit FIFO High
Byte field represents the upper byte of the
transmit FIFO location currently addressed by
the Transmit FIFO Write Pointer (TWP). In 8-
bit mode, the ATFH field is not used.
20.7.4 Audio Transmit DMA Register n (ATDRn)
The ATDRn register contains the data to be transmitted in
slot n, assigned for DMA support. In 8-bit mode, only the
lower 8-bit portion of the ATDRn register is used, and the
upper byte is ignored (not transferred into the ATSR). In 16-
bit mode, the whole 16-bit word is transferred into the ATSR.
The CPU bus master, typically a DMA controller, has write-
only access to the transmit DMA registers. After reset, these
registers are clear.
ATDL The Audio Transmit DMA Low Byte field holds
the lower byte of the audio data.
ATDH In 16-bit mode, the Audio Transmit DMA High
Byte field holds the upper byte of the audio
data word. In 8-bit mode, the ATDH field is ig-
nored.
7 0
ARFL
15 8
ARFH
7 0
ARDL
15 8
ARDH
7 0
ATFL
15 8
ATFH
7 0
ATDL
15 8
ATDH