153 www.national.com
CP3BT26
20.7.5 Audio Global Configuration Register (AGCR)
The AGCR register controls the basic operation of the inter-
face. The CPU bus master has read/write access to the
AGCR register. After reset, this register is clear.
ASS The Asynchronous/Synchronous Mode Se-
lect bit controls whether the audio interface
operates in Asynchronous or in Synchronous
mode. After reset the ASS bit is clear, so the
Synchronous mode is selected by default.
0 – Synchronous mode.
1 – Asynchronous mode.
DWL The Data Word Length bit controls whether
the transferred data word has a length of 8 or
16 bits. After reset, the DWL bit is clear, so 8-
bit data words are used by default.
0 – 8-bit data word length.
1 – 16-bit data word length.
LPB The Loop Back bit enables the loop back
mode. In this mode, the SRD and STD pins
are internally connected. After reset the LPB
bit is clear, so by default the loop back mode
is disabled.
0 – Loop back mode disabled.
1 – Loop back mode enabled.
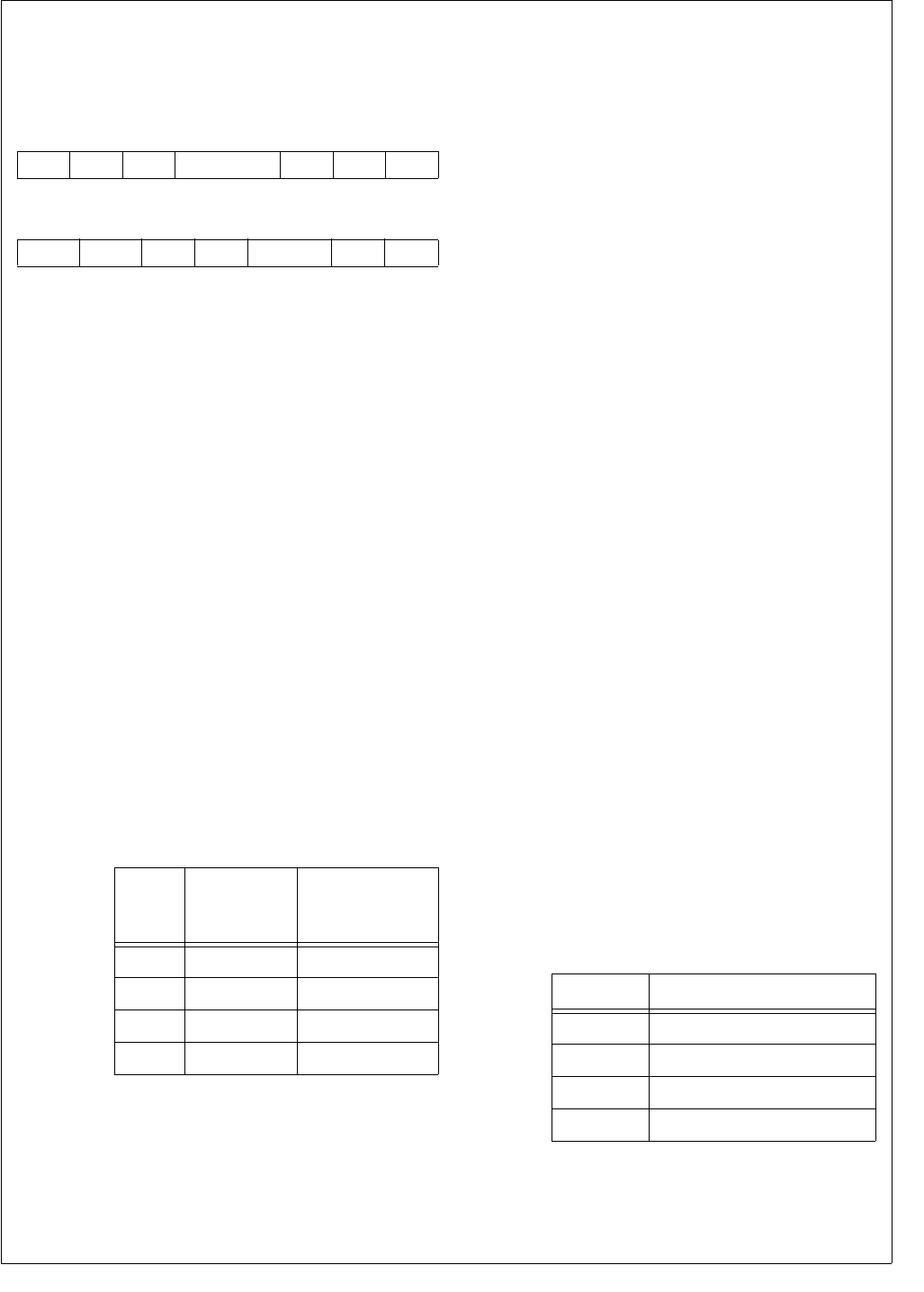
SCS The Slot Count Select field specifies the num-
ber of slots within each frame. If the number of
slots per frame is equal to 1, the audio inter-
face operates in normal mode. If the number
of slots per frame is greater than 1, the inter-
face operates in network mode. After reset all
SCS bits are cleared, so by default the audio
interface operates in normal mode.
IEFS The Internal/External Frame Sync bit controls,
whether the frame sync signal for the receiver
and transmitter are generated internally or
provided from an external source. After reset,
the IEFS bit is clear, so the frame synchroni-
zation signals are generated internally by de-
fault.
0 – Internal frame synchronization signal.
1 – External frame synchronization signal.
FSS The Frame Sync Select bit controls whether
the interface (receiver and transmitter) uses
long or short frame synchronization signals.
After reset the FSS bit is clear, so short frame
synchronization signals are used by default.
0 – Short (bit length) frame synchronization
signal.
1 – Long (word length) frame synchronization
signal.
IEBC The Internal/External Bit Clock bit controls
whether the bit clocks for receiver and trans-
mitter are generated internally or provided
from an external source. After reset, the IEBC
bit is clear, so the bit clocks are generated in-
ternally by default.
0 – Internal bit clock.
1 – External bit clock.
CRF The Clear Receive FIFO bit is used to clear
the receive FIFO. When this bit is written with
a 1, all pointers of the receive FIFO are set to
their reset state. After updating the pointers,
the CRF bit will automatically be cleared
again.
0 – Writing 0 has no effect.
1 – Writing 1 clears the receive FIFO.
CTF The Clear Transmit FIFO bit is used to clear
the transmit FIFO. When this bit is written with
a 1, all pointers of the transmit FIFO are set to
their reset state. After updating the pointers,
the CTF bit will automatically be cleared
again.
0 – Writing 0 has no effect.
1 – Writing 1 clears the transmit FIFO.
FSL The Frame Sync Length field specifies the
length of the frame synchronization signal,
when a long frame sync signal (FSS = 1) and
a 16-bit data word length (DWL = 1) are used.
If an 8-bit data word length is used, long frame
syncs are always 6 bit clocks in length.
IFS The Inverted Frame Sync bit controls the po-
larity of the frame sync signal.
0 – Active-high frame sync signal.
1 – Active-low frame sync signal.
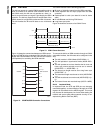
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
IEBC FSS IEFS SCS LPB DWL ASS
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
CLKEN AAIEN IOM2 IFS FSL CTF CRF
SCS
Number of
Slots per
Frame
Mode
00 1 Normal mode
01 2 Network mode
10 3 Network mode
11 4 Network mode
FSL Frame Sync Length
00 13 bit clocks
01 14 bit clocks
10 15 bit clocks
11 16 bit clocks