Flash Memory Segmentation
5-3 Flash Memory Controller
5.2 Flash Memory Segmentation
MSP430 flash memory is partitioned into segments. Single bits, bytes, or
words can be written to flash memory, but the segment is the smallest size of
flash memory that can be erased.
The flash memory is partitioned into main and information memory sections.
There is no difference in the operation of the main and information memory
sections. Code or data can be located in either section. The differences
between the two sections are the segment size and the physical addresses.
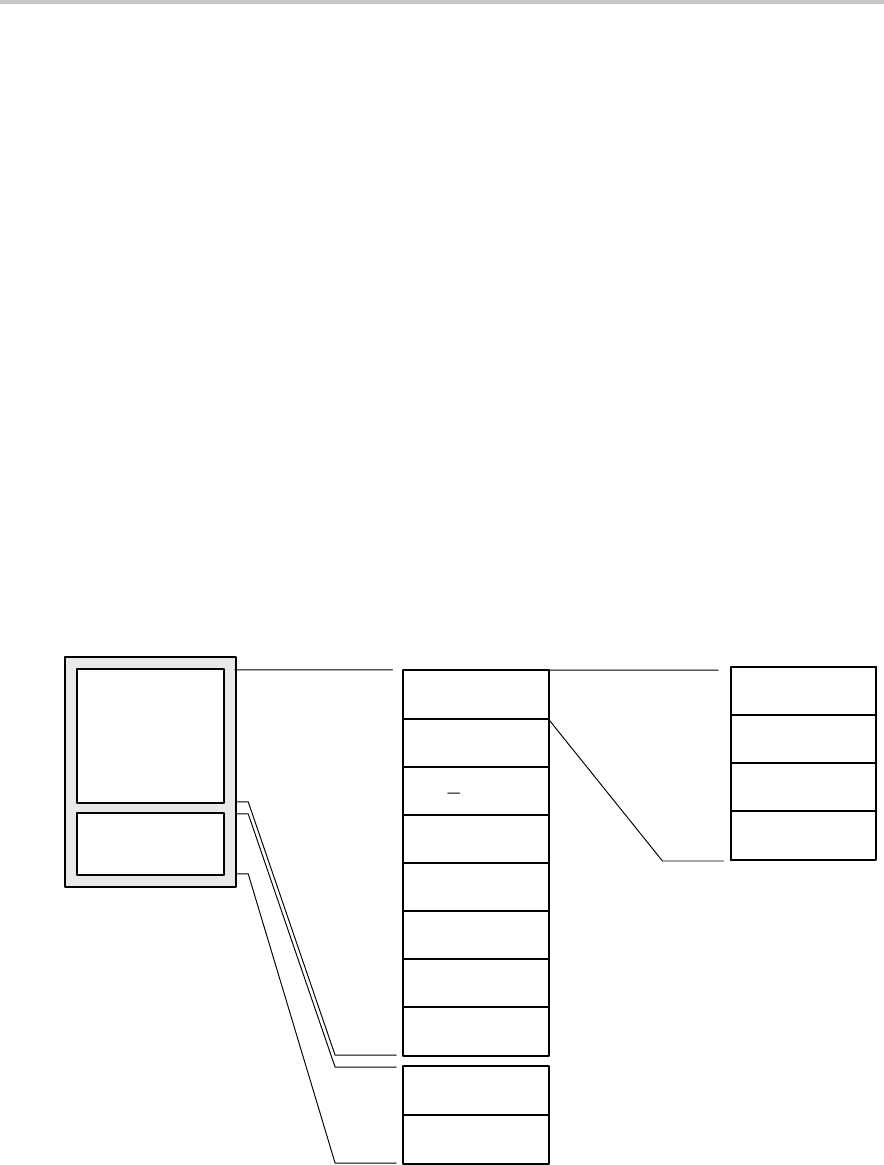
The information memory has two 128-byte segments. The main memory has
two or more 512-byte segments. See the device-specific datasheet for the
complete memory map of a device.
The segments are further dividing into blocks. A block is 64 bytes, starting at
0xx00h, 0xx40h, 0xx80h, or 0xxC0h, and ending at 0xx3Fh, 0xx7Fh, 0xxBFh,
or 0xxFFh.
Figure 5−2 shows the flash segmentation using an example of 4-KB flash that
has eight main segments and both information segments.
Figure 5−2. Flash Memory Segments, 4-KB Example
FFFFh
F000h
10FFh
1000h
Segment0
Segment1
Segment2
Segment3
Segment4
Segment5
Segment6
Segment7
SegmentA
SegmentB
FFFFh
F000h
10FFh
1000h
FE00h
FDFFh
FC00h
256-byte
Flash
Information Memory
4-kbyte
Flash
Main Memory
4 KB + 256 byte
xx3Fh
xx00h
Block
Block
Block
Block
xxFFh
xxBFh
xx7Fh
xxC0h
xx80h
xx40h