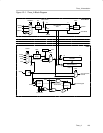
Timer_A Operation
12-8 Timer_A
Use of the Continuous Mode
The continuous mode can be used to generate independent time intervals and
output frequencies. Each time an interval is completed, an interrupt is
generated. The next time interval is added to the TACCRx register in the
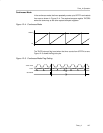
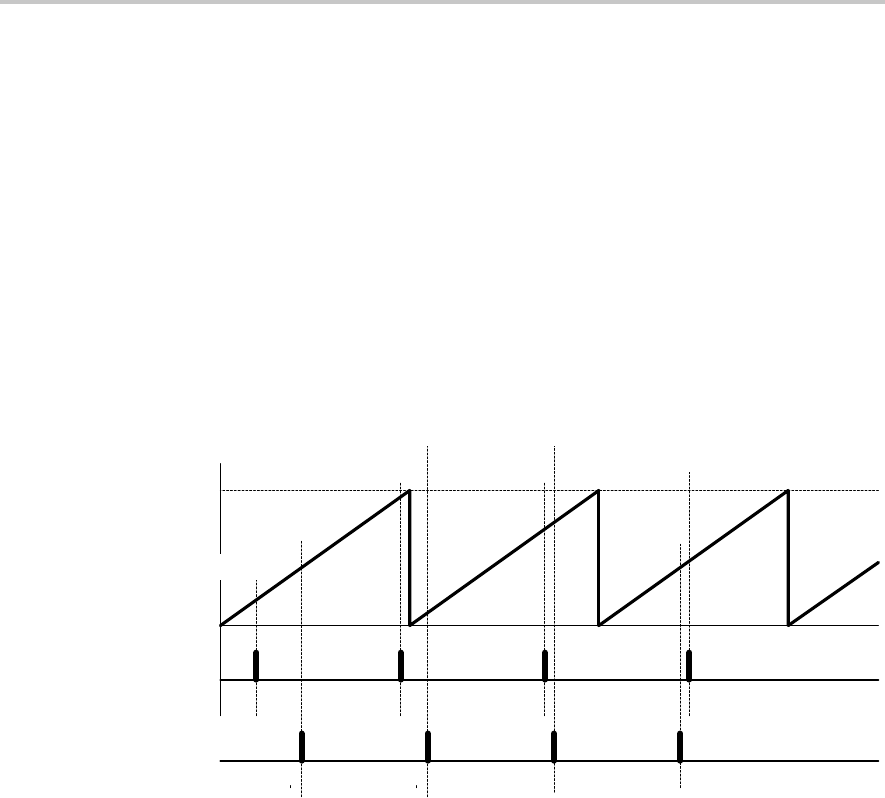
interrupt service routine. Figure 12−6 shows two separate time intervals t
0
and
t
1
being added to the capture/compare registers. In this usage, the time
interval is controlled by hardware, not software, without impact from interrupt
latency. Up to three (Timer_A3) or five (Timer_A5) independent time intervals
or output frequencies can be generated using capture/compare registers.
Figure 12−6. Continuous Mode Time Intervals
0FFFFh
TACCR0a
TACCR0b TACCR0c
TACCR0d
t
1
t
0
t
0
TACCR1a
TACCR1b TACCR1c
TACCR1d
t
1
t
1
t
0
Time intervals can be produced with other modes as well, where TACCR0 is
used as the period register. Their handling is more complex since the sum of
the old TACCRx data and the new period can be higher than the TACCR0
value. When the previous TACCRx value plus t
x
is greater than the TACCR0
data, the TACCR0 value must be subtracted to obtain the correct time interval.