Appendix
88
9
❒ Default access settings 1 and 2 are
as follows:
❖
❖❖
❖ Display
Shows SNMP information and
available protocols.
msh> snmp ?
The following command displays
the settings of registered number
specified.
msh> snmp [registered_number]
Omitting the number displays all
access settings.
msh> snmp [-p]
Note
❒ Add “-p” (as above) to have the
information displayed one
screen at a time.
❖
❖❖
❖ Community name configuration
You can set the community name
of the registered number.
msh> snmp number name
community_name
Note
❒ The community name can con-
sist of up to 15 characters.
❖
❖❖
❖ Access type configuration
You can select the access type from
those listed below:
msh> snmp number type
access_type
❖
❖❖
❖ Protocol configuration
You should use the following com-
mand to set protocols to active or
inactive. If you set a protocol to in-
active, all access settings for that
protocol will be disabled:
msh> snmp {ip | ipx}
{on | off}
•“on” means active, “off” means
inactive.
To change an access setting proto-
col, use the following command.
However, if you have disabled a
protocol using the above com-
mand, making it active here will
have no effect.
msh> snmp number active
{ip | ipx} {on | off}
❖
❖❖
❖ Access configuration
You can configure a host address
according to protocols used.
The network interface board ac-
cepts requests only from hosts
with “read-only” or “read-write”
access type addresses. Enter “0” to
have the network interface board
accept requests from any host
without requiring a specific type of
access.
msh> snmp number
{ip | ipx} address
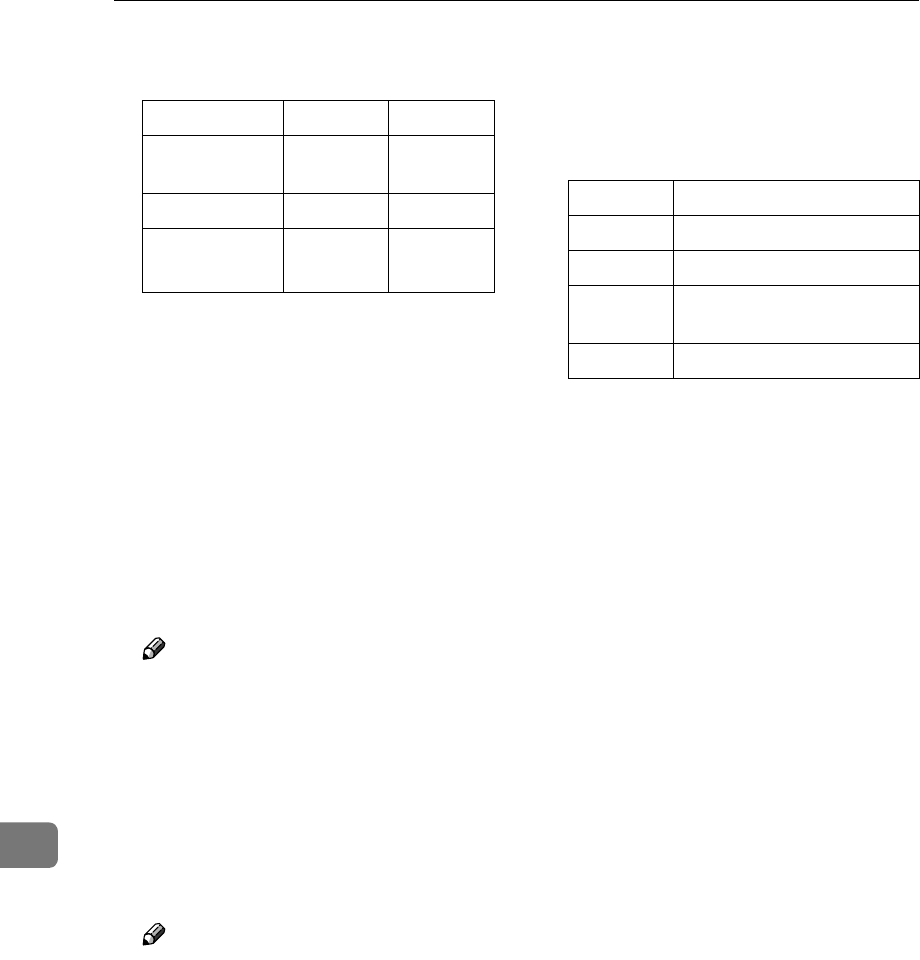
Number 1 2
Community
name
public admin
IP address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Access type read-only
trap off
read-write
trap off
Access type
Type of access permitted
read Read only
write Read and write
trap User notified of trap mes-
sages.
no All access denied.


















