Appendix
96
9
DNS
Use the “dns” command to configure
or display DNS (Domain Name Sys-
tem) settings.
❖
❖❖
❖ View setting
The following command displays
current DNS settings:
msh> dns
❖
❖❖
❖ Using the DNS server obtained from
the DHCP server
The following command ena-
bles/disables use the DNS server
obtained from the DHCP server:
msh> dns dhcp
{valid | invalid}
• If you use the DNS server ob-
tained from the DHCP server,
select “valid”. If not, select
“invalid”.
If you set “valid”, the DNS serv-
er from the DHCP server is pri-
oritized.
❖
❖❖
❖ DNS server configuration
The following command ena-
bles/disables use of the DNS serv-
er address:
msh> dns number server
server_address
The following is a sample configu-
ration using an IP address of
192.168.15.16 on DNS 1 server:
msh> dns 1 server
192.168.15.16
• You can register up to three
DNS server numbers.
•
You cannot use “255.255.255.255”
as the DNS server address.
Domain name
Use the “domainname” command to
display or configure domain name
settings.
You can configure the Ethernet inter-
face, IEEE 1394 interface, or IEEE
802.11b interface.
❖
❖❖
❖ View setting
The following command displays
the current domain name:
msh> domainname
❖
❖❖
❖ Interface domain configuration
The following command displays
or sets the Ethernet interface do-
main name, IEEE 1394 interface, or
IEEE 802.11b interface.
msh> domainname interface_
name domain_name
The following is a sample configu-
ration using a domain name on the
Ethernet interface:
msh> domainname ether
domain_name
*1
Available when the optional 1394
interface board is installed.
*2
Available when the optional
802.11b interface unit is installed.
Note
❒ A domain name can consist of
up to 63 alphanumeric charac-
ters.
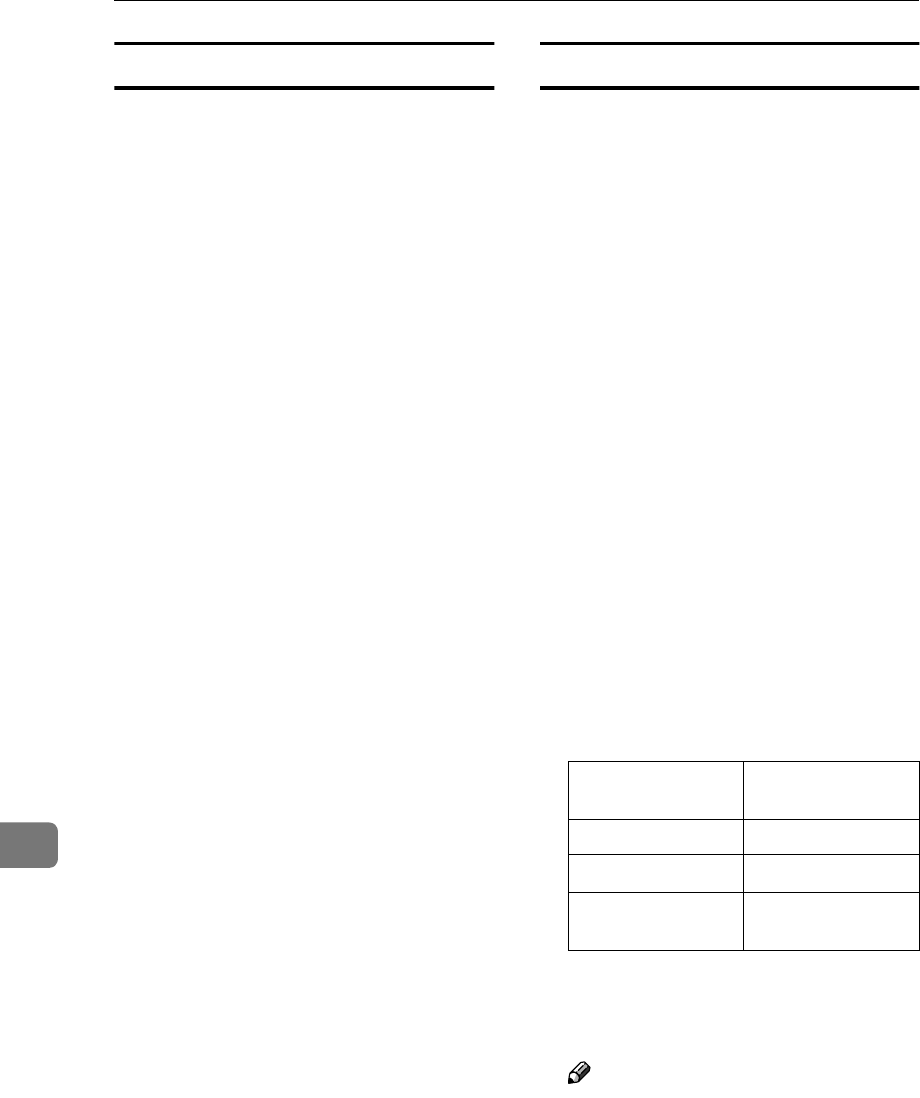
Interface Interface that can
be set
ether Ethernet interface
ip1394
*1
IEEE 1394 interface
wlan
*2
IEEE 802.11b inter-
face


















