Theory of Operation
1780R-Series Service Manual
3–15
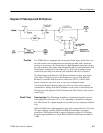
Diagram 6 Vertical Deflection
The current output of the filters passes through a common base amplifier which
drives a Gilbert multiplier (Variable Gain Amplifier). Output current from the
Variable Gain Amplifier drives inputs to two separate differential amplifiers (X1
and X5). The other side of the differential amplifiers is driven by the Vertical
Position voltage.
Vertical readout information from the Microprocessor is input through a third
differential amplifier. Only one of the three differential amplifiers (X1, X5, or
Readout) is operational at a given time. The output drives a Limiter and the
Deflection Amplifier to drive the CRT deflection plates. Limiting is required to
prevent the Deflection Amplifier from going into saturation or cut off.
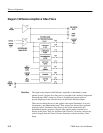
Variable Gain. Q619 is a common base amplifier whose voltage output drives
U515 whose gain is controlled by the voltage between pins 8 and 10. U411B is a
–5 volt voltage source, and R513 is a longtailed current source. The voltage
between pins 8 and 10 of U515 is determined by manipulating the current
balance in Q514 through the voltage across R509. The Variable Gain Centering,
R514, is adjusted for a 450 mV calibrator signal amplitude in WFM+CAL mode
of operation. The Variable Gain Registration, R510, is adjusted so that there is
no output DC movement of a composite video signal when the variable
WAVEFORM GAIN control is varied.
The output current of the Gain Cell (U515) passes through cascode transistors
Q518 and Q519 to drive the X1/X5 Amplifier.
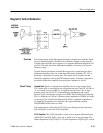
X1/X5 Amplifier. The X1/X5 Amplifier consists of two separate differential pairs
(Q520-Q321 and Q521-Q421), only one of which is on at any given time. The
emitter impedance of Q521-Q421 is 1/5 of the impedance of Q520-Q321, which
Overview
Circuit Theory