User’s Manual
IBM PowerPC 750GX and 750GL RISC Microprocessor
gx_02.fm.(1.2)
March 27, 2006
Programming Model
Page 117 of 377
2.3.5.4 Optional External Control Instructions
The PowerPC Architecture defines an optional external control feature that, if implemented, is supported by
the two external control instructions, eciwx and ecowx. These instructions allow a user-level program to
communicate with a special-purpose device. The instructions provided are summarized in Table 2-39.
The eciwx and ecowx instructions let a system designer map special devices in an alternative way. The
MMU translation of the EA is not used to select the special device, as it is used in most instructions such as
loads and stores. Rather, it is used as an address operand that is passed to the device over the address bus.
Four other signals (the burst and size signals on the 60x bus) are used to select the device; these four signals
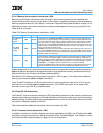
Data Cache Block Store dcbst rA,rB
The EA is computed, translated, and checked for protection violations.
• For cache hits with the tag marked exclusive unmodified (E), no further
action is taken.
• For cache hits with the tag marked M, the cache block is written back to
memory and marked exclusive unmodified (E).
A dcbst is not broadcast unless HID0[ABE] = 1 regardless of WIMG settings.
The instruction acts like a load with respect to address translation and memory
protection. It executes regardless of whether the cache is disabled or locked.
The exception priorities (from highest to lowest) for dcbst are as follows:
1 BAT protection violation–DSI exception
2 TLB protection violation–DSI exception.
Data Cache Block Flush dcbf rA,rB
The EA is computed, translated, and checked for protection violations.
• For cache hits with the tag marked exclusive modified (M), the cache block
is written back to memory and the cache entry is invalidated.
• For cache hits with the tag marked exclusive unmodified (E), the entry is
invalidated.
• For cache misses, no further action is taken.
A dcbf is not broadcast unless HID0[ABE] = 1 regardless of WIMG settings.
The instruction acts like a load with respect to address translation and memory
protection. It executes regardless of whether the cache is disabled or locked.
The exception priorities (from highest to lowest) for dcbf are as follows:
1 BAT protection violation—DSI exception
2 TLB protection violation—DSI exception.
Instruction Cache Block
Invalidate
icbi rA,rB
This instruction performs a virtual lookup into the instruction cache (index only).
The address is not translated, so it cannot cause an exception. All ways of a
selected set are invalidated regardless of whether the cache is disabled or
locked. The
750GX never broadcasts icbi onto the 60x bus.
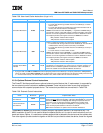
Table 2-39. External Control Instructions
Name Mnemonic Syntax Implementation Notes
External Control In
Word Indexed
eciwx rD,rA,rB
A transfer size of 4 bytes is implied. The TBST
and TSIZ[0–2] signals are rede-
fined to specify the Resource ID (RID), copied from bits EAR[28–31]. For these
operations, TBST
carries the EAR[28] data. Misaligned operands for these
instructions cause an alignment exception. Addressing a location where
SR[T] = 1 causes a DSI exception. If MSR[DR] = 0, a programming error
occurs and the physical address on the bus is undefined.
Note: These instructions are optional in the PowerPC Architecture.
External Control Out
Word Indexed
ecowx rS,rA,rB
Table 2-38. User-Level Cache Instructions (Page 2 of 2)
Name Mnemonic Syntax Implementation Notes
1. A program that uses dcbt and dcbtst instructions improperly performs less efficiently. To improve performance, HID0[NOOPTI]
can be set, which causes dcbt and dcbtst to be no-oped at the cache. These instructions do not cause bus activity and cause only
a 1-clock execution latency. The default state of this bit is zero, which enables the use of these instructions.