User’s Manual
IBM PowerPC 750GX and 750GL RISC Microprocessor
Instruction Timing
Page 244 of 377
gx_06.fm.(1.2)
March 27, 2006
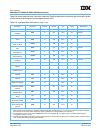
Table 6-9 shows load-and-store instruction latencies. Pipelined load/store instructions are shown with cycles
of total latency and throughput cycles separated by a colon.
Table 6-9. Load-and-Store Instructions (Page 1 of 4)
Instruction Mnemonic
Primary
Opcode
Extended
Opcode
Unit Cycles Serialization
Data Cache Block Flush dcbf 31 86 LSU 3:5
1
Execution
Data Cache Block
Invalidate
dcbi 31 470 LSU 3:3
1
Execution
Data Cache Block Store dcbst 31 54 LSU 3:5
1
Execution
Data Cache Block
Touch
dcbt 31 278 LSU 2:1 —
Data Cache Block
Touch for Store
dcbtst 31 246 LSU 2:1 —
Data Cache Block set to
Zero
dcbz 31 1014 LSU 3:6
12
Execution
External Control In
Word Indexed
eciwx 31 310 LSU 2:1 —
External Control Out
Word Indexed
ecowx 31 438 LSU 2:1 —
Instruction Cache Block
Invalidate
icbi 31 982 LSU 3:4
1
Execution
Load Byte and Zero lbz 34 — LSU 2:1 —
Load Byte and Zero with
Update
lbzu 35 — LSU 2:1 —
Load Byte and Zero with
Update Indexed
lbzux 31 119 LSU 2:1 —
Load Byte and Zero
Indexed
lbzx 31 87 LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Double
lfd 50 — LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Double with Update
lfdu 51 — LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Double with Update
Indexed
lfdux 31 631 LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Double Indexed
lfdx 31 599 LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Single
lfs 48 — LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Single with Update
lfsu 49 — LSU 2:1 —
Load Floating-Point
Single with Update
Indexed
lfsux 31 567 LSU 2:1 —
1. For cache operations, the first number indicates the latency in finishing a single instruction; the second indicates the throughput for
back-to-back cache operations. Throughput might be larger than the initial latency, as more cycles might be needed to complete
the instruction to the cache, which stays busy keeping subsequent cache operations from executing.
2. The throughput number of six cycles for dcbz assumes it is to nonglobal (M = 0) address space. For global address space,
throughput is at least 11 cycles.
3. Load/store multiple/string instruction cycles are represented as a fixed number of cycles plus a variable number of cycles, where n
is the number of words accessed by the instruction.