Rev.1.10 Jul 01, 2005 page 82 of 318
REJ09B0124-0110
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 11. DMAC
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
11. DMAC
The DMAC (Direct Memory Access Controller) allows data to be transferred without the CPU intervention.
Two DMAC channels are included. Each time a DMA request occurs, the DMAC transfers one (8- or 16-bit)
data from the source address to the destination address. The DMAC uses the same data bus as used by the
CPU. Because the DMAC has higher priority of bus control than the CPU and because it makes use of a
cycle steal method, it can transfer one word (16 bits) or one byte (8 bits) of data within a very short time after
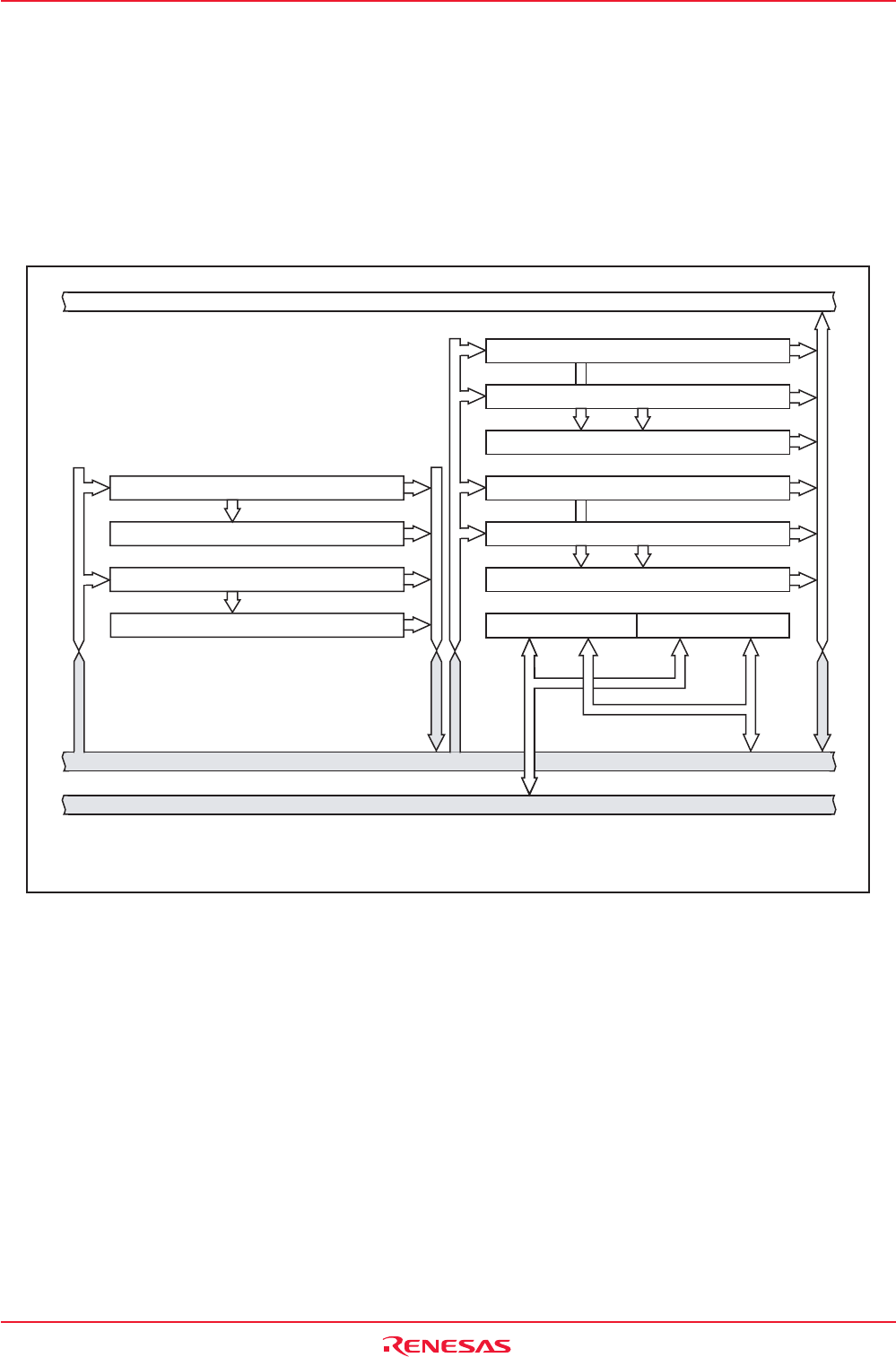
a DMA request is generated. Figure 11.1 shows the block diagram of the DMAC. Table 11.1 shows the
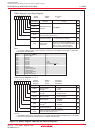
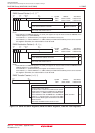
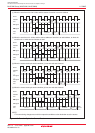
DMAC specifications. Figures 11.2 to 11.4 show the DMAC related-registers.
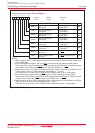
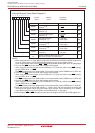
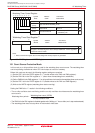
Figure 11.1 DMAC Block Diagram
A DMA request is generated by a write to the DSR bit in the DMiSL register (i = 0, 1), as well as by an
interrupt request which is generated by any function specified by the DMS and DSEL3 to DSEL0 bits in the
DMiSL register. However, unlike in the case of interrupt requests, DMA requests are not affected by the I flag
and the interrupt control register, so that even when interrupt requests are disabled and no interrupt request
can be accepted, DMA requests are always accepted. Furthermore, because the DMAC does not affect
interrupts, the IR bit in the interrupt control register does not change state due to a DMA transfer.
A data transfer is initiated each time a DMA request is generated when the DMAE bit in the DMiCON register
= 1 (DMA enabled). However, if the cycle in which a DMA request is generated is faster than the DMA
transfer cycle, the number of transfer requests generated and the number of times data is transferred may
not match. For details, refer to 11.4 DMA Request.
Data bus low-order bits
DMA latch high-order bits
DMA latch low-order bits
DMA0 source pointer SAR0
DMA0 destination pointer DAR0
DMA0 forward address pointer
(1)
Data bus high-order bits
Address bus
DMA1 destination pointer DAR1
DMA1 source pointer SAR1
DMA1 forward address pointer
(1)
NOTE:
1.Pointer is incremented by a DMA request.
DMA0 transfer counter reload register TCR0
DMA0 transfer counter TCR0
DMA1 transfer counter reload register TCR1
DMA1 transfer counter TCR1