Configuring Switching Information 413
DHCP Relay VLAN Configuration
You can enable L2 DHCP relay on a particular VLAN. The VLAN is identified by a service VLAN ID (S-
VID), which a service provider uses to identify a customer’s traffic while traversing the provider network
to multiple remote sites. The switch uses the VLAN membership of the switch port client (the customer
VLAN ID, or C-VID) to perform a lookup a corresponding S-VID.
If the S-VID is enabled for DHCP Relay, then the packet can be forwarded. If the C-VID does not
correspond to an S-VID that is enabled for DHCP Relay, then the switch will not relay the DHCP request
packet.
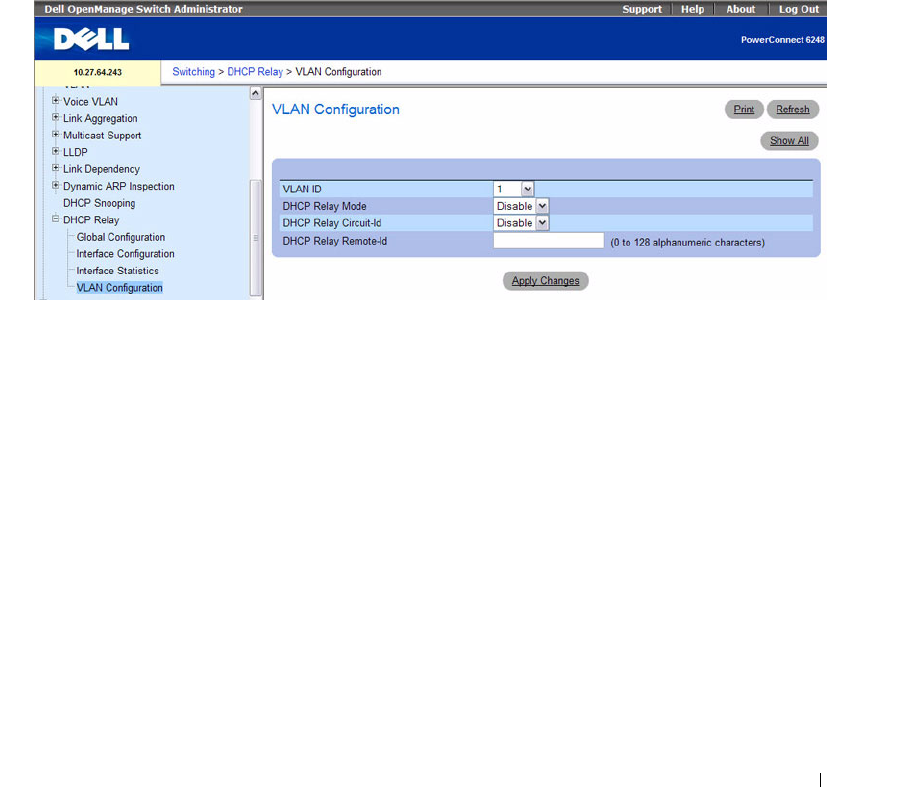
To access this page, click Switching > DHCP Relay > VLAN Configuration in the tree view.
Figure 7-127. DHCP Relay VLAN Configuration
The DHCP Relay VLAN Configuration page contains the following fields:
•
VLAN ID
— Select a VLAN ID from the list for configuration. This is an S-VID (as indicated by the
service provider) that identifies a VLAN that is authorized to relay DHCP packets through the provider
network.
•
DHCP Relay Mode
— Enable or disable the selected VLAN for DHCP Relay services. The default is
Disable
.
•
DHCP Relay Circuit-Id
— When enabled, if a client sends a DHCP request to the switch and the
client is in a VLAN that corresponds to the selected S-VID, the switch adds the client’s interface
number to the Circuit ID sub-option of Option 82 in the DHCP request packet. The default is
Disable
.
This enables the switch to reduce the broadcast domain to which the server replies are switched when
the broadcast bit is set for DHCP packets. When this bit is set, the server is required to echo the
Option-82 in replies. Since the circuit-id field contains the client interface number, the L2 relay agent
can forward the response to the requesting interface only, rather to all ports in the VLAN).