XG2000 series User's Guide
40/315
All Rights Reserved, Copyright (C) PFU LIMITED 2009
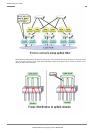
4.6.1 Port Roles Based on Spanning Tree
RSTP assigns one of these port roles to individual ports:
z Root port
Provides the best path (lowest cost) when the switch forwards packets to the root switch.
z Designated port
Connects to the designated switch toward the leaves of the spanning tree. The port specified
connecting to the designated port serves as a root port.
z Alternate Port
The alternative port with the second lowest path cost. In the event that the root port goes
to a linkdown state, the alternate port serves as the root port. It does not always send
or receive frames while in the blocking state.
z Backup Port
Provides an alternative path to that specified. In the event that the specified port goes
into a linkdown state, the backup port serves as the new designated port. It does not always
send or receive frames while it is in the blocking state.
z Disabled Port
Disabled port, it does not send or receive any frames.
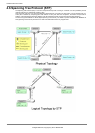
4.6.2 Spanning Tree Protocol Port States
The port states defined by the STP are:
z Discard
The port is in a "discarding state. BPDUs are only received.
z Learn
The port is in a "learning" state. A port in the learning state learns the destination MAC
address of the received frames but does not participate in frame forwarding.
z Forward
The port is ready to transmit data traffic.
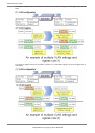
The STP states "blocking" and "listening" have been merged into a unique RSTP "discarding" state. The correspondence
between STP port states and RSTP port states are shown below.
Display
Format
STP(IEEE802.1D) RSTP(IEEE802.1w)
Discard Blocking Discarding
Discard Listening Discarding
Learn Learning Learning
Forward Forwarding Forwarding
4.6.3 Configuring Spanning Tree
To configure the spanning tree protocol, carry out the following procedure in the administrator EXEC mode.
Command Task
xg# configure terminal
Switch to global configuration mode.
xg(config)# spanning-tree
Enable Spanning Tree Protocol.
xg(config)# spanning-tree priority <0-61440>
xg(config)# spanning-tree hello-time <1-10>
xg(config)# spanning-tree max-age <6-40>
xg(config)# spanning-tree forward-time <4-30>
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol parameters on the
device.
z Switch priority
z Hello time
z Maximum aging time (max-age)
z Forward delay time (forward-time)
xg(config)# interface port 1 2 3
xg(config)# interface port range 1 3
Switch to interface edit mode to configure spanning
tree-related parameters for a given port.
In this example, the global interface configuration mode
is selected for ports 1 through 3.
xg(config-if)# spanning-tree port-priority
<0-240>
xg(config-if)# spanning-tree port-path-cost
<1-200000000>
Configure the following parameters related to the
spanning tree topology:
z Port priority
z Path cost
xg(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
(Optional)
If the port is configured as an edge port(*), this setting
can reduce the time taken to transition into the
forwarding state.
* It is available only when the port is directly connected
to an end terminal that has no influence on the spanning
tree configuration.
xg(config-if)# exit
Exit to global configuration mode.
xg(config)# exit
Exit to administrator EXEC mode.
xg# show spanning-tree [ detail ]
View the state of the spanning tree.