A wide area network (WAN) is usually distinguished from a local area network
(LAN) in that physical communications is limited to two systems. The
communications line between the two systems can be a direct connection such as a
leased telephone line. However, it is more common to connect two systems by a
dial-up telephone connection. A dial-up connection between systems is also known
as a switched connection. For a switched line, the connection turns on or off
depending on whether a phone connection has been established. In the case of a
leased line, the connection between the two systems is always available.
PPP versus SLIP
Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) is the result of early attempts to connect two
systems using TCP/IP over an asynchronous line. SLIP is described in Request for
Comment (RFC) 1055,
A Nonstandard For Transmission of IP Datagrams Over
Serial Lines: SLIP
. This RFC defines a simple framing method for IP packets
flowing over a serial line. SLIP is not an Internet standard.
The SLIP RFC never became an Internet standard because it has several
deficiencies that are discussed in the RFC. Some of those deficiencies are as
follows:
v No standardized mechanism for hosts to communicate addressing information
v No support for network protocols other than TCP/IP
v No support for system authentication
v No support for packet error detection, error correction, or compression
While SLIP is still used today, IBM does not encourage you to use it. PPP corrects
all of the SLIP deficiencies. PPP is an Internet standard and the predominant
connection protocol used today among Internet Service Providers.
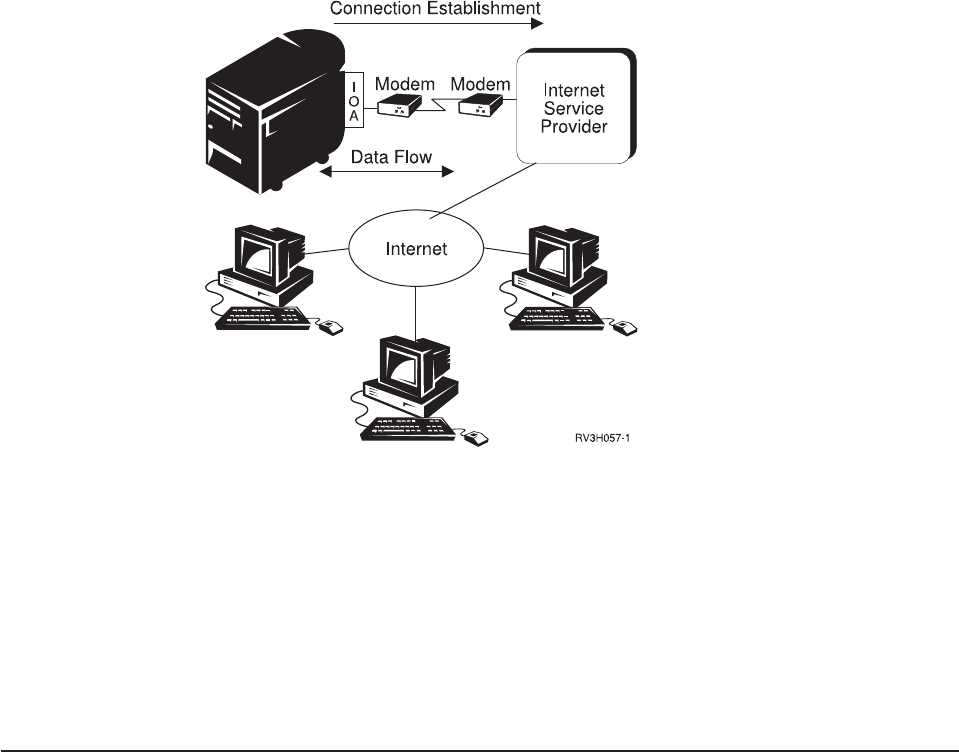
Figure 72. AS/400 Dial-out to an ISP
94 OS/400 TCP/IP Configuration and Reference V4R4


















