settings or required system objects. The MSG-type strings occur on unexpected
errors. Since these are not anticipated, they usually occur because of unanticipated
circumstances or customer environments not seen during development and test.
The exact location in the code for MSG-type errors must be determined from other
information.
As part of the goal to provide quick turnaround for error isolation, the server takes
the additional step of dumping the job log (DMPJOBLOG) and job information
(DMPJOB) to spooled files on all FFDC errors. Therefore, two spooled files will be
generated for these conditions. These dumps are done at the time of error, and are
done by the signal handler function. The primary reason for doing this is to get
relevant information immediately following the error, before the job is ended.
The actual spooled file dump commands are:
QSYS/DSPJOBLOG JOB(*) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
QSYS/DSPJOB OUTPUT(*PRINT)
These spooled files are owned by the QTMTWSG user profile.
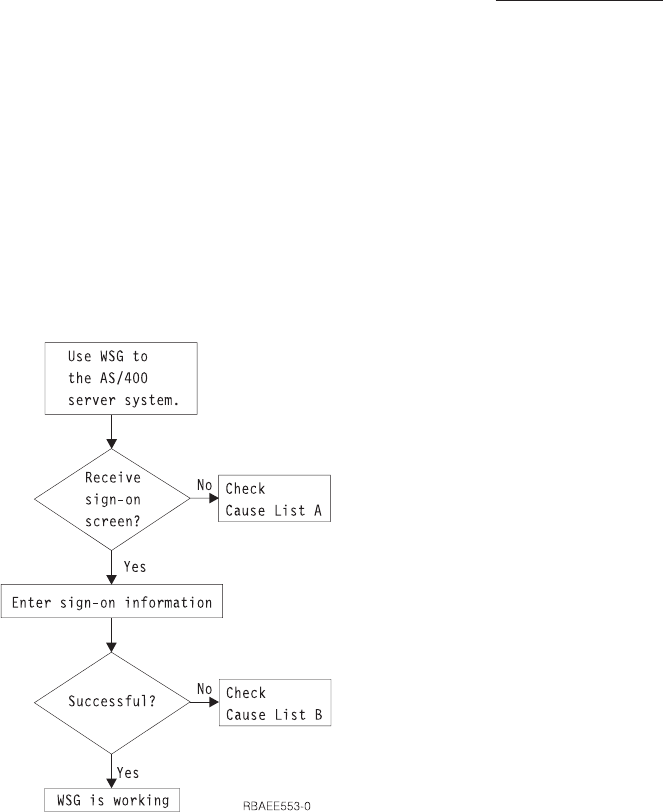
If a problem is detected when using the AS/400 WSG server, use the following flow
chart to identify the cause after using the flow chart for general TCP/IP problems
(Figure 247 on page 431). The cause lists that follow identify potential problems.
Cause List A
1. Verify that the QAUTOVRT system value on the AS/400 server system is
properly set to allow automatic creation of virtual devices. For example, to allow
the creation of 50 virtual devices enter the command:
CHGSYSVAL SYSVAL(QAUTOVRT) VALUE(50)
2. Verify that the virtual devices on the AS/400 server system that are used by
WSG are defined to a subsystem under which the interactive jobs should run.
Use the Display Subsystem Description (DSPSBSD) command to see which
Figure 281. WSG Server Problem Analysis
Chapter 21. TCP/IP Problem Analysis 481


















