2. The failing point-to-point session job log.
3. The type and model of the modem used and the modem strings selected.
4. A copy of the options used in the failing point-to-point profile.
5. A copy of the parameter values used in the line description.
6. The connection dialog script being used (if one is being used)
7. The connection dialog script spooled file output (if it exists)
8. A copy of any QSYSOPR messages that may have been logged concerning the
SLIP connection
9. A communications trace of the failing SLIP connection (if possible).
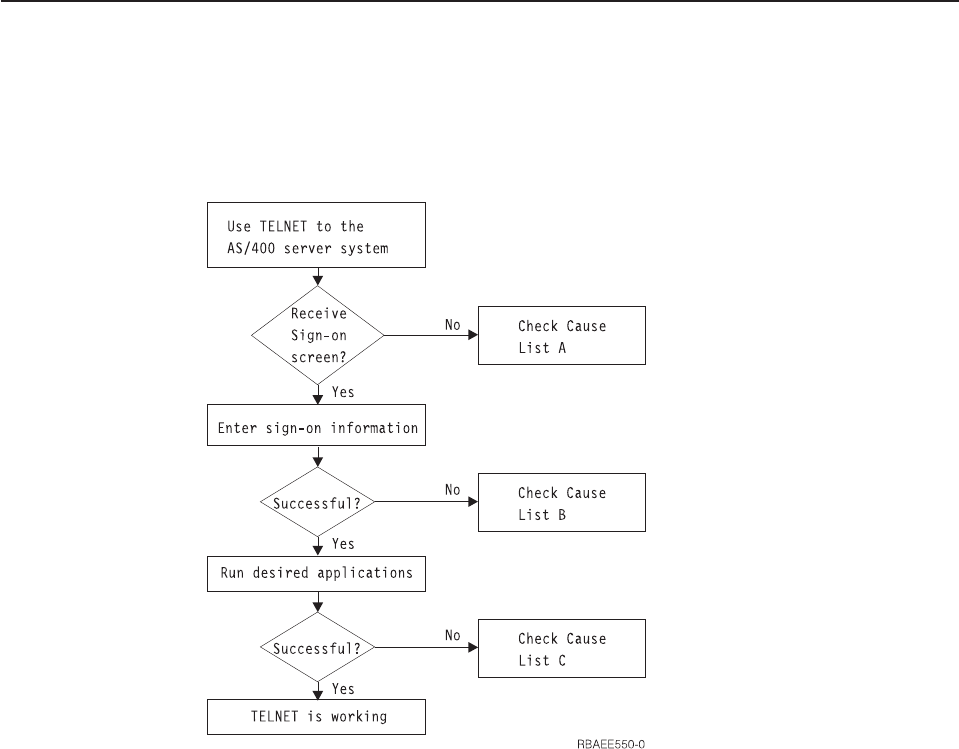
Determining Problems with TELNET
If a problem is detected when using the AS/400 TELNET server, use the following
flow chart to identify the cause after using the flow chart for general TCP/IP
problems. (Figure 247 on page 431). The cause lists that follow identify potential
problems.
Cause List A
1. Verify that the Telnet server jobs are active and that Telnet service is assigned
to a valid non-restricted port. Use the WRKACTJOB command to verify that
QTVTELNET and QTVDEVICE jobs are active in QSYSWRK subsystem. If
these jobs are not active, use the STRTCPSVR *TELNET command to start
these jobs. Use NETSTAT *CNN to verify that Telnet service is assigned to a
valid port.
2. Verify that the QAUTOVRT system value on the AS/400 server system is
properly set to allow the TELNET server to automatically create virtual devices.
For example, to allow the creation of 50 virtual devices enter the command:
Figure 253. TELNET Server Problem Analysis
Chapter 21. TCP/IP Problem Analysis 443
|
|
|
|
|
|


















