The old default character mapping tables, QTCPEBC (see Table 66 on page 528)
and QTCPASC ( Table 67 on page 528), remain on the AS/400 system. These
mapping tables can be used by specifying the following:
v For TELNET ASCII line mode, specify QUSRSYS/QTCPASC for the TBLVTOUT
parameter and QUSRSYS/QTCPEBC for the TBLVTIN parameter.
v For FTP client, specify QUSRSYS/QTCPASC for the TBLFTPOUT parameter and
QUSRSYS/QTCPEBC for the TBLFTPIN parameter.
v For FTP server, specify QUSRSYS/QTCPASC for the TBLFTPOUT parameter
and QUSRSYS/QTCPEBC for the TBLFTPIN parameter. The FTP server must
be ended and started for this change to take effect.
TCP/IP supports both ASCII and several variations of EBCDIC character sets. The
tables in this section describe the character sets and the mapping between them.
Table 62 and Table 63 describe the EBCDIC character set and code page that are
shipped with the system.
Note: Table 62 and Table 63 are used only if ASCII-to-EBCDIC or
EBCDIC-to-ASCII mapping tables cannot be found or generated based on
the current national language. Refer to the
International Application
Development
for the 037 (EBCDIC) code page.
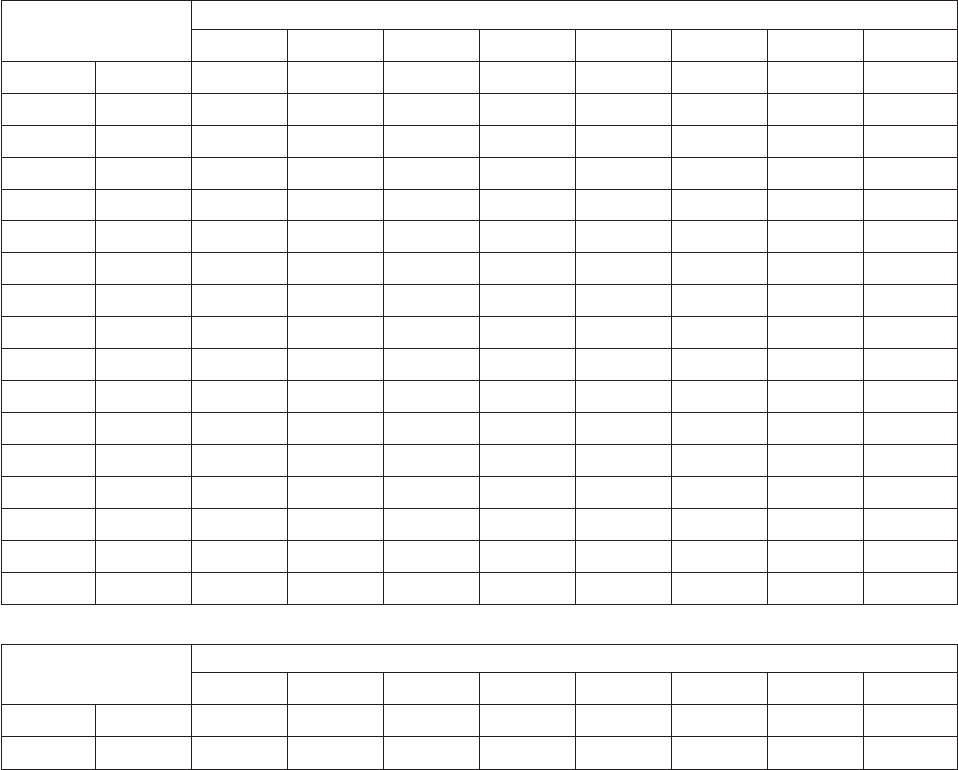
Table 62. EBCDIC Character Set
Main Storage Bit
Positions 4,5,6,7
Main Storage Bit Positions 0,1,2,3
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111
Hex01234567
0000 0 NUL DLE SP &; -
0001 1 SOH DC1 /
0010 2 STX DC2 SYN
0011 3 ETX DC3
0100 4
0101 5 HT NL LF
0110 6 BS ETB
0111 7 DEL ESC EOT
1000 8 CAN
1001 9 EM ’
1010 A ! :
1011 B VT . $ , #
1100 C FF FS DC4 < * % @
1101 D CR GS ENQ NAK ( ) _ ’
1110 E SO RS ACK + ; > =
1111 F SI US BEL SUB | | ? ″
Table 63. EBCDIC Character Set
Main Storage Bit
Positions 4,5,6,7
Main Storage Bit Positions 0,1,2,3
1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
Hex 8 9 A B C D E F
0000 0 { } \ 0
Appendix C. Mapping Tables Associated with TCP/IP Function 525


















