A network to which a node system is physically connected is a local network for
that system. A network that a system reaches only after passing through one or
more IP routers is called a remote network.
Internetwork Communications
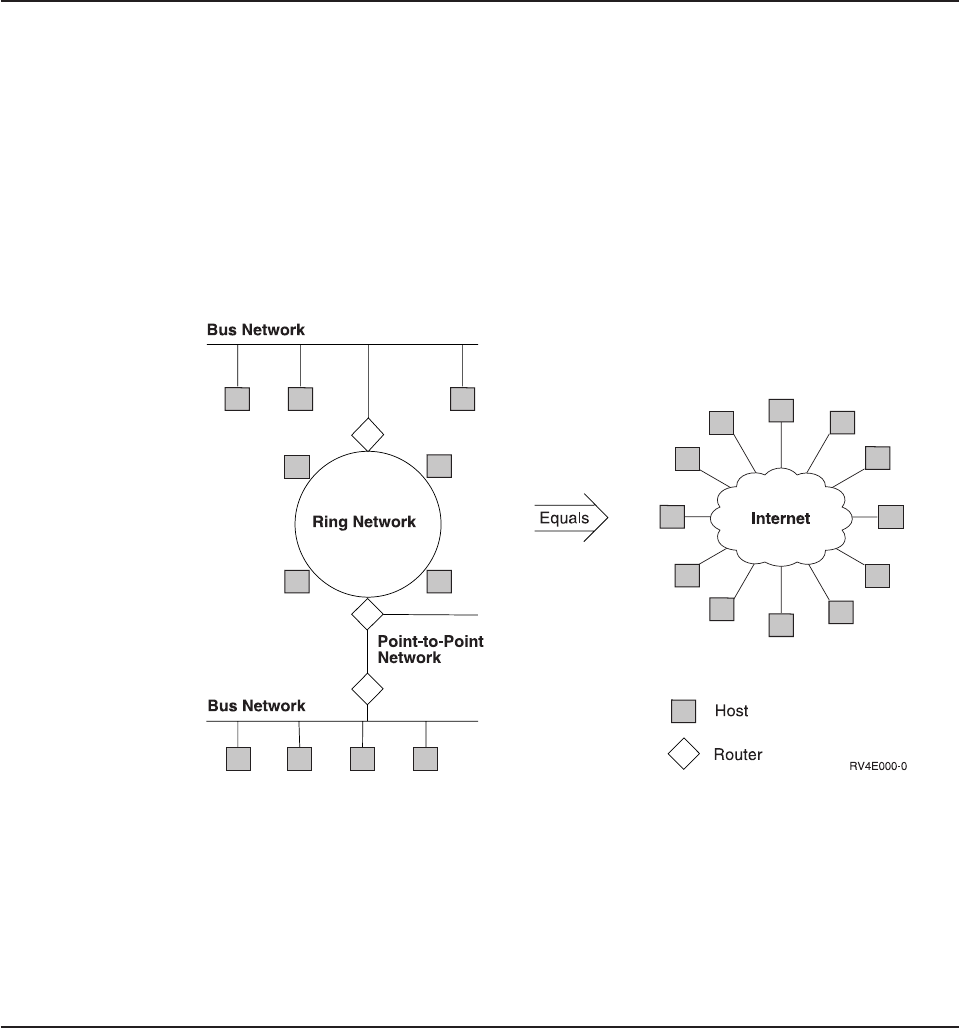
An internetwork or internet is a collection of packet-switched physical networks that
are connected by routers to form a single, large virtual network. Simply, it is a
network of networks. Packets are units of data that are sent across
packet-switched networks. All nodes in the internet communicate as if they are on
the same physical network, regardless of their specific hardware or specific
software architecture. This cooperation among otherwise incompatible networks and
systems is known as
interoperability
.
Figure 2 shows how networks can be connected in an internet.
The network connection of each node on an internetwork is assigned a unique
address. This internet address differs from a physical hardware address in that the
hardware address is often preset by the manufacturer, whereas you can assign or
reassign an internet address by standard conventions. Also, internet addresses are
in a standard form, while different hardware types use different address lengths and
formats.
Internet Addresses
Each node on a network is known as a
host
and has a unique address called an
internet address
. This address is a 32-bit integer. An address is expressed in the
form nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn, where each field is the decimal representation of one byte,
or 8 bits, of the address. For example, the address whose hexadecimal
representation is X'82638001' is expressed as 130.99.128.1.
Figure 2. An Internetwork
2 OS/400 TCP/IP Configuration and Reference V4R4


















