250
Example 16
The largest modification index (4.727) suggests allowing eps2 and eps4 to be
correlated in the control group. (Eps2 and eps4 are already correlated in the
experimental group.) Making this modification leads to Model C.
Model C
Model C is just like Model B except that the terms eps2 and eps4 are correlated in both
the control group and the experimental group.
To specify Model C, just take Model B and remove the constraint on the covariance
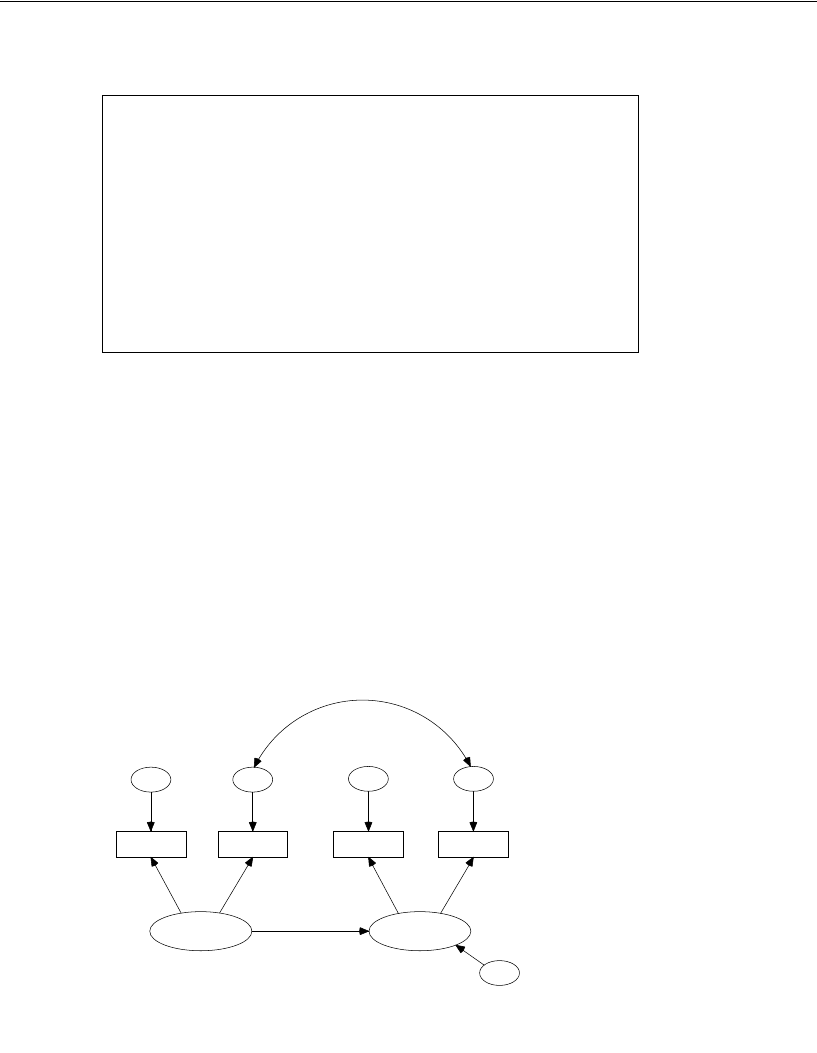
between eps2 and eps4 in the control group. Here is the new path diagram for the
control group, as found in file Ex16-c.amw:
Modification Indices (control - Default model)
Covariances: (control - Default model)
M.I. Par Change
eps2
<-->
eps4
4.727
2.141
eps1
<-->
eps4
4.086
-2.384
Variances: (control - Default model)
M.I. Par Change
Regression Weights: (control - Default model)
M.I. Par Change
Means: (control - Default model)
M.I. Par Change
Intercepts: (control - Default model)
M.I. Par Change
0,
pre_verbal
a_syn1
pre_syn
0,
eps1
1
1
a_opp1
pre_opp
0,
eps2
opp_v1
1
0
post_verbal
a_syn2
post_syn
0,
eps3
a_opp2
post_opp
0,
eps4
1
1
opp_v2
1
0,
zeta
1
Example 16: Model C
An alternative to ANCOVA
Olsson (1973): control condition.
Model Specification


















