Chapter 3: Applications and Configuration Overview
Avidia System Configuration and Management User Manual 57
OAM ALARMS AND LOOPBACKS
Operation, Administration and Maintenance (OAM) provides a set of standard functions that
the network uses for fault management that:
• surveys alarms
• performs loopback tests (connectivity verification)
• provides continuity checks between ATM devices
OAM testing is not disruptive to ATM virtual channels (VPCs and VCCs), which makes it ideal
for testing and troubleshooting live ATM networks. OAM cells are carried in the same VPCs
and VCCs that carry end-user traffic; therefore, the VPCs and VCCs remain active while
performing OAM ATM-layer testing.
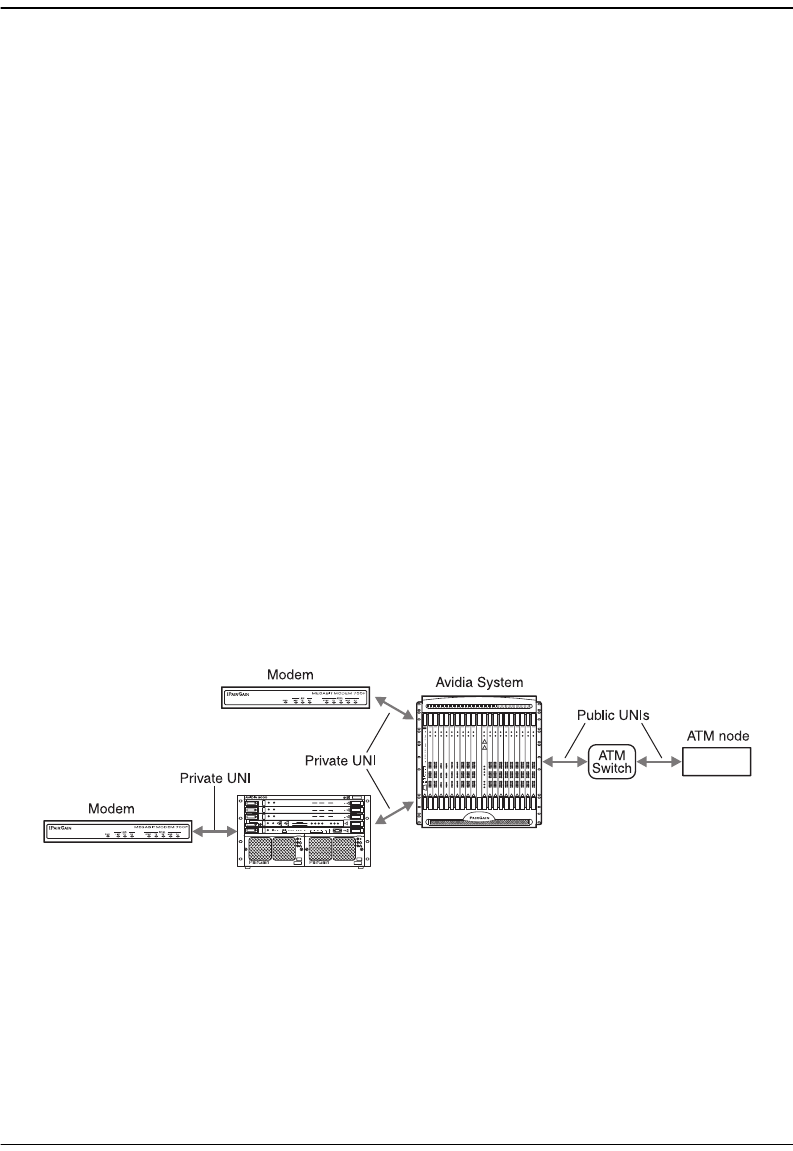
Avidia systems support OAM management functions across the User-Network Interface (UNI)
which can be either public (Avidia to an ATM network switch) or private (Avidia to Avidia
or Avidia to a modem). Avidia systems can both respond to and generate OAM cells. Avidia
implements these OAM flows:
• F4, which provides ATM-layer management functions at a VPC level
• F5, which provides ATM-layer management functions at a VCC level
The following figure shows connections that the OAM management functions can test.
About Alarm Surveillance
When the physical layer detects an error such as loss of signal or loss of cell synchronization, a
VPC or VCC failure is indicated to the ATM layer with an Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) and
a Remote Defect Indicator (RDI). When the Avidia system receives an AIS, it responds with an
RDI. Both signals contain a field that specifies the type of failure and where the failure occurred.


















