ARM INSTRUCTION SET S3C2440A RISC MICROPROCESSOR
3-56
COPROCESSOR REGISTER TRANSFERS (MRC, MCR)
The instruction is only executed if the condition is true. The various conditions are defined in Table 3-2. The
instruction encoding is shown in Figure 3-27.
This class of instruction is used to communicate information directly between ARM920T and a coprocessor. An
example of a coprocessor to ARM920T register transfer (MRC) instruction would be a FIX of a floating point value
held in a coprocessor, where the floating point number is converted into a 32 bit integer within the coprocessor,
and the result is then transferred to ARM920T register. A FLOAT of a 32 bit value in ARM920T register into a
floating point value within the coprocessor illustrates the use of ARM920T register to coprocessor transfer (MCR).
An important use of this instruction is to communicate control information directly from the coprocessor into the
ARM920T CPSR flags. As an example, the result of a comparison of two floating point values within a coprocessor
can be moved to the CPSR to control the subsequent flow of execution.
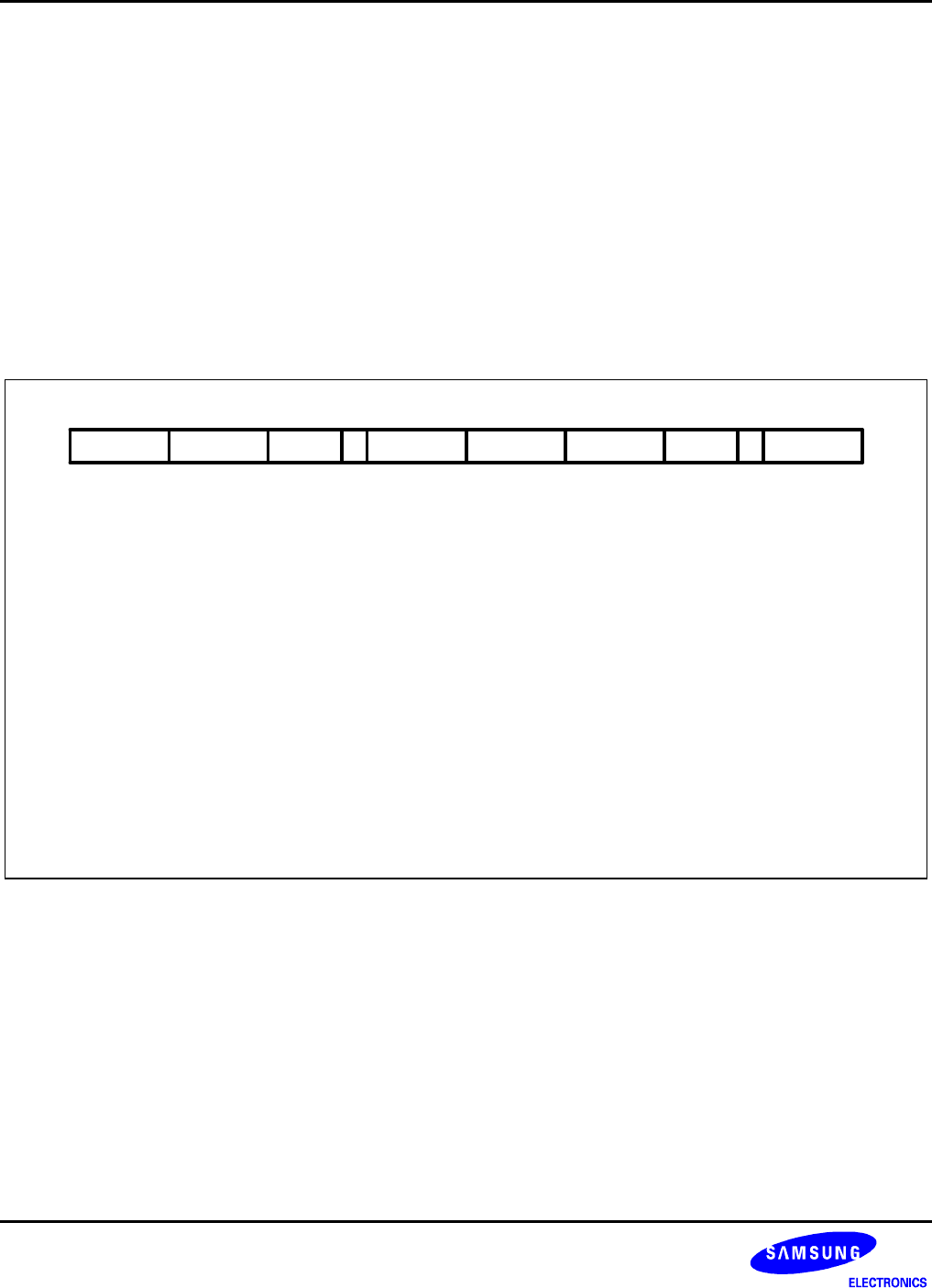
31 27 19 15
Cond
28 16 11122123 20
L CRn Rd
[3:0] Coprocessor Operand Register
[7:5] Coprocessor Information
[11:8] Coprocessor Number
[15:12] ARM Source/Destination Register
[19:16] Coprocessor Source/Destination Register
[20] Load/Store Bit
0 = Store to coprocessor
1 = Load from coprocessor
[21] Coprocessor Operation Mode
[31:28] Condition Field
1110 CP Opc CP#
24
CRm1CP
87 543 0
Figure 3-27. Coprocessor Register Transfer Instructions
THE COPROCESSOR FIELDS
The CP# field is used, as for all coprocessor instructions, to specify which coprocessor is being called upon.
The CP Opc, CRn, CP and CRm fields are used only by the coprocessor, and the interpretation presented here is
derived from convention only. Other interpretations are allowed where the coprocessor functionality is incompatible
with this one. The conventional interpretation is that the CP Opc and CP fields specify the operation the
coprocessor is required to perform, CRn is the coprocessor register which is the source or destination of the
transferred information, and CRm is a second coprocessor register which may be involved in some way which
depends on the particular operation specified.


















