512 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
8992APPA.DOC TI-89 / TI-92 Plus: Appendix A (US English) Susan Gullord Revised: 02/23/01 1:48 PM Printed: 02/23/01 2:21 PM Page 512 of 132
tanh
ê
(squareMatrix1)
⇒
squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse hyperbolic
tangent of
squareMatrix1
. This is
not
the same
as calculating the inverse hyperbolic tangent
of each element. For information about the
calculation method, refer to
cos()
.
squareMatrix1
must be diagonalizable. The
result always contains floating-point
numbers.
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular
complex format mode:
tanh
ê
([1,5,3;4,2,1;6,
ë
2,1])
¸
ë
.099…+.164…
ø
i
.267…
ì
1.490…
ø
i
…
ë
.087…
ì
.725…
ø
i
.479…
ì
.947…
ø
i
…
.511…
ì
2.083…
ø
i
ë
.878…+1.790…
ø
i
…
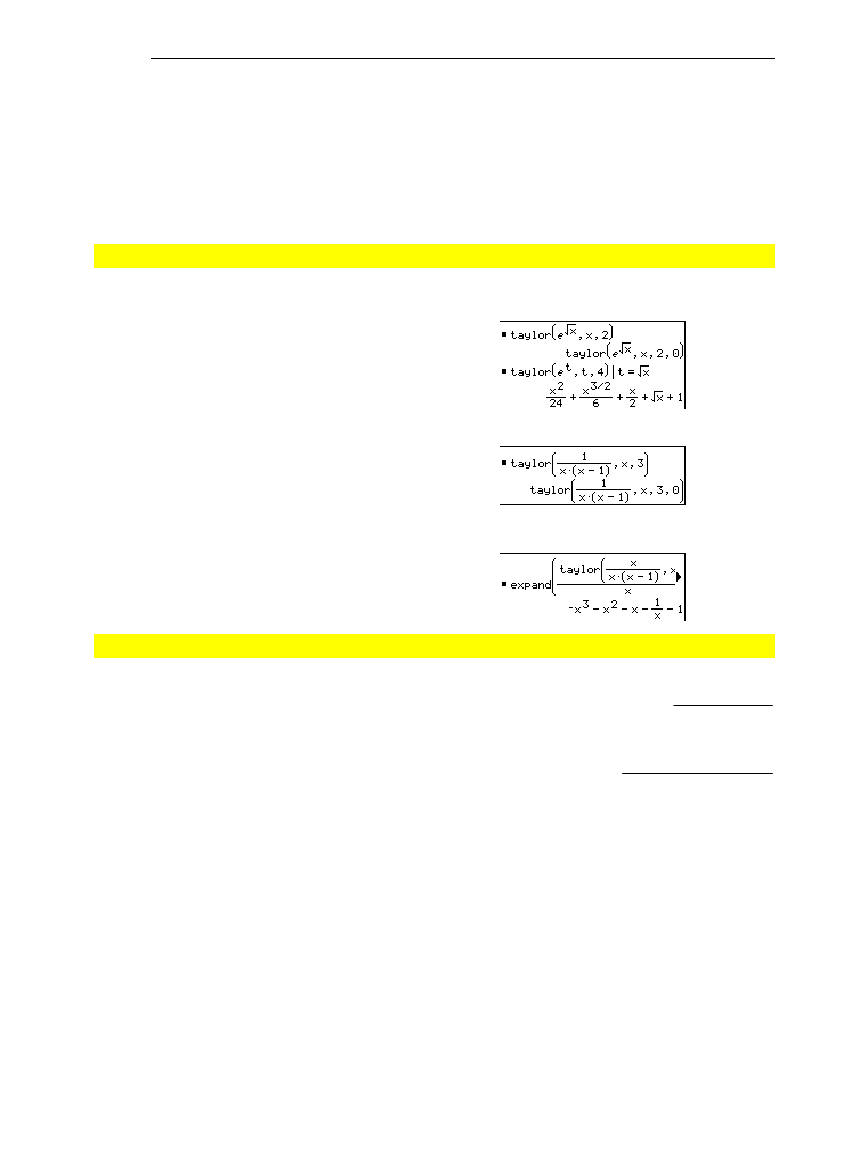
taylor()
MATH/Calculus menu
taylor(expression1, var, order
[
, point
]
)
⇒
expression
Returns the requested Taylor polynomial.
The polynomial includes non-zero terms of
integer degrees from zero through
order
in
(
var
minus
point
).
taylor()
returns itself if
there is no truncated power series of this
order, or if it would require negative or
fractional exponents. Use substitution and/or
temporary multiplication by a power of
(
var
minus
point
) to determine more general
power series.
point
defaults to zero and is the expansion
point.
taylor(
e
^(‡(x)),x,2)
¸
taylor(
e
^(t),t,4)|t=‡(x)
¸
taylor(1/(x
ù
(x
ì
1)),x,3)
¸
expand(taylor(x/(x
ù
(x
ì
1)),
x,4)/x,x)
¸
tCollect()
MATH\Algebra\Trig menu
tCollect(expression1)
⇒
expression
Returns an expression in which products and
integer powers of sines and cosines are
converted to a linear combination of sines
and cosines of multiple angles, angle sums,
and angle differences. The transformation
converts trigonometric polynomials into a
linear combination of their harmonics.
Sometimes
tCollect()
will accomplish your
goals when the default trigonometric
simplification does not.
tCollect()
tends to
reverse transformations done by
tExpand()
.
Sometimes applying
tExpand()
to a result
from
tCollect()
, or vice versa, in two separate
steps simplifies an expression.
tCollect((cos(a))^2)
¸
cos(2
ø
a)
+
1
2
tCollect(sin(a)cos(b))
¸
sin(a
ì
b)+sin(a+b)
2


















