80 Chapter 3: Symbolic Manipulation
03SYMBOL.DOC TI-89/TI-92 Plus: Symbolic Manipulation (English) Susan Gullord Revised: 02/23/01 10:52 AM Printed: 02/23/01 2:12 PM Page 80 of 24
These indicate the result
of an identity or a
Boolean expression.
This notation indicates
an “arbitrary integer”
that represents any
integer.
When an arbitrary
integer occurs multiple
times in the same
session, each
occurrence is numbered
consecutively. After it
reaches 255, arbitrary
integer consecutive
numbering restarts at
@n0. Use
Clean Up
2:NewProb
to reset to
@n1
.
ˆ represents infinity,
and
e
represents the
constant
2.71828...
(base of the natural
logarithms).
These constants are
often used in entries as
well as results.
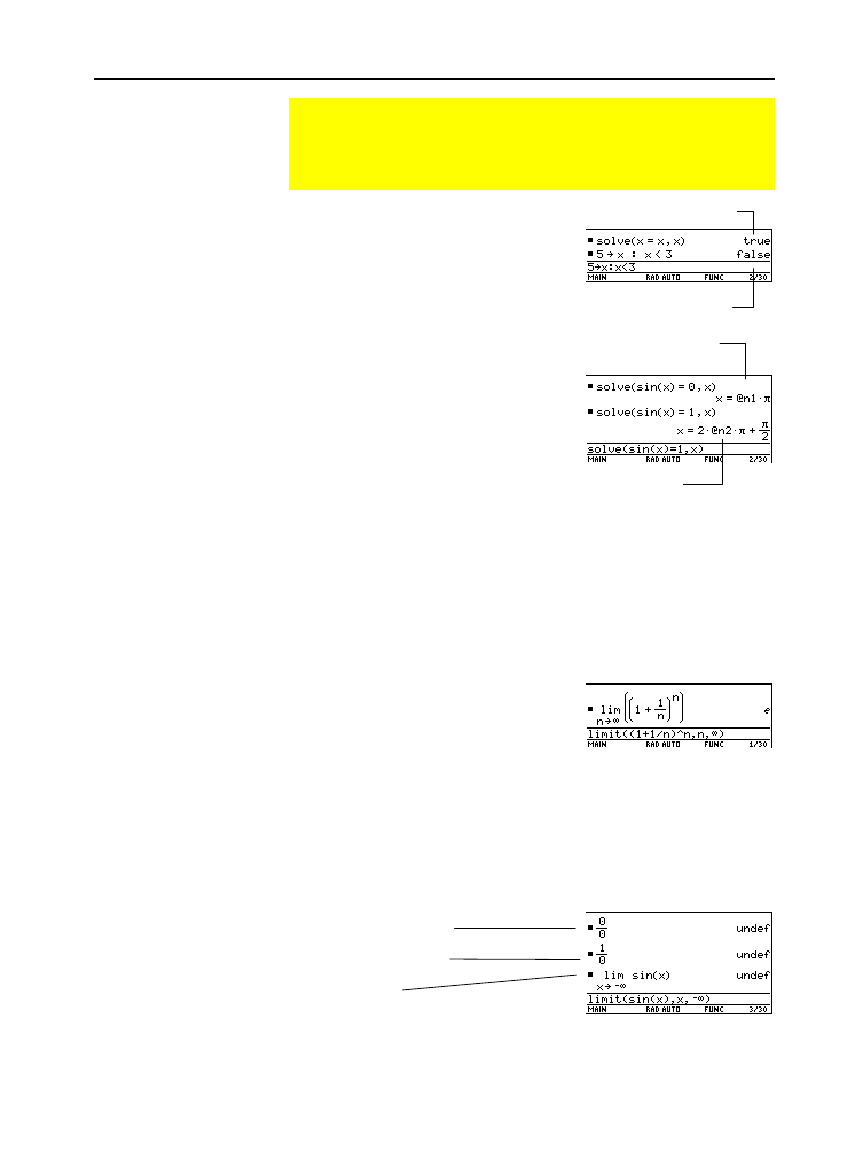
This indicates that the result is undefined.
Special Constants Used in Symbolic Manipulation
The result of a calculation may include one of the special
constants described in this section. In some cases, you may
also need to enter a constant as part of your entry.
true, false
@
n1 ... @n255
For @, press:
TI
.
89
:
¥§
TI
.
92 Plus
:
2
R
ˆ
,
e
For
ˆ
, press:
TI.89
:
¥
*
TI.92 Plus:
2
*
For
e
, press:
TI.89:
¥
s
TI.92 Plus:
2
s
undef
x=x is true for any value of x.
5<3 is false.
Both @n1 and @n2 represent
any arbitrary integer, but this
notation identifies separate
arbitrary integers.
A solution is at every integer
multiple of
p
.
„ˆ
(undetermined sign)
Mathematically undefined
Non-unique limit


















