The ARM-TRIG
State Diagram
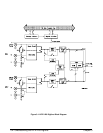
The state diagram of Figure 3-4 shows that the digitizer operates within four
states: idle, initiated, wait-for-arm, and wait-for-trigger. The path through
the states depends upon whether pre-arm sampling is part of the
measurement configuration.
Both paths begin with the digitizer in the idle state. The digitizer enters the
idle state when power is applied, or following a reset or an ABORt. This is
the state in which the digitizer is configured using CONFigure and its
low-level commands.
Note When configuring the digitizer’s arming and triggering hardware the
configuration applies to both digitizer channels. Thus, both channels enter
the same Arm-Trigger state at the same time. In arming and triggering
commands where a channel can be specified such as
SENSe[<
chan
>]:SWEep:OFFSet:POINts <
count
>
the configuration of the last channel specified (or implied) overrides the
previous configuration of both channels.
The Pre-Arm Path The digitizer is capable of pre-arm and post-arm sampling. If pre-arm
samples (readings) have been specified
(SENSe[<chan >]:SWEep:OFFSet:POINts <count >) in addition to
post-arm samples, the digitizer moves to the wait-for-trigger state when
INITiate[:IMMediate] is executed and begins sampling. The digitizer
continues to (pre-arm) sample until the pre-arm reading count is reached
and until the digitizer receives an arm signal. When the arm is received, the
digitizer begins post-arm sampling as triggers are received. The digitizer
continues to (post-arm) sample until the total number of samples (pre- and
post-arm) specified by TRIGger[:STARt]:COUNt <count > is reached.
Once the trigger count is reached, the digitizer determines if the arm count
has been reached. If it has not, the digitzer remains initiated and repeats the
path until the arm count is reached.
The Post-Arm Path When only post-arm samples are specified, the digitizer moves to the
wait-for-arm state when INITiate[:IMMediate] is executed. The digitizer
moves to the wait-for-trigger state when an arm signal is received. The
digitizer remains in the wait-for-trigger state until the number of samples
specified by TRIGger[:STARt]:COUNt <count > is reached. Once the
trigger count is reached, the digitizer determines if the arm count has been
reached. If it has not, the digitizer remains initiated and repeats the path
until the arm count is reached.
112 Understandin
g
the HP E1429 Di
g
itizer Chapter 3