Retrieving
Readings Using
READ?
The most common method of retrieving readings from the digitizer is using
the READ? subsystem which consists of the command:
READ[<chan >]?
The <chan > parameters are:
1 - returns readings from channel 1 (default channel)
2 - returns readings from channel 2
READ? is equivalent to executing the following sequence of commands:
• ABORt - aborts the readings after the arm count and trigger count is
reached.
• INITiate - places the digitizer in wait-for-arm state.
• FETCh[<chan >]? - retrieves the readings from memory and places
them on the VME (VXI data transfer) bus.
As a result, READ? is used for applications that require readings to be
immediately available to a computer, rather than remaining in digitizer
memory.
Because each READ? initiates the digitizer, executing READ1? followed
by READ2? causes the digitizer to take two sets of measurements. If it is
necessary to obtain readings from both channels during the same period, use
INIT and FETCh? which are described in the next section.
Retrieving
Readings Using
FETCh?
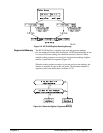
One method of retrieving readings from memory involves the digitizer’s
FETCh? command shown below. FETChing readings from memory places
them on the VME (VXI data transfer) bus
(Figure 3-11).
FETCh[<
chan
>]?
:COUNt?
:RECover?
FETChing Readings
from Memory
Recall that the HP E1429 digitizer samples both channels simultaneously
and stores the readings as a single 24-bit number (Figure 3-8). Using the
FETCh? command, each channel’s readings can be retrieved from memory
individually.
Chapter 3 Understandin
g
the HP E1429 Di
g
itizer 139