The Questionable
Signal Status Group
The digitizer’s Questionable Signal status group monitors overload
conditions, the frequency accuracy of the divide-by-n reference source, and
error conditions in non-volatile calibration memory.
The Condition Register Overload conditions, divide-by-n frequency accuracy, and non-volatile
calibration memory errors are monitored with the following bits in the
Condition register. All other bits are unused.
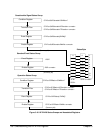
1514131211109876543210
unused CAL unused TIME VOLT
VOLTage: Bit 0 is set (1) if an amplifier overrange (single-ended or
differential input) is detected during a measurement sequence. Otherwise,
the bit remains cleared (0).
TIME: Bit 2 is set (1) when the divide-by-n reference source cannot
generate a sample rate that is within 1% of the rate specified by
TRIG:TIMer1 or TRIG:TIMer2. Otherwise, the bit remains cleared (0).
CALibration: Bit 8 is set (1) when an error is detected in non-volatile
calibration memory.
Reading the Condition Register
The current state of bits 0, 2, and 8 can be determined by reading the
Condition register with the command:
STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Bit 0 has a corresponding decimal value of 1, bit 2 has a decimal value of 4,
and bit 8 has a decimal value of 256. Reading the Condition register does
not affect the bit settings. The bits are cleared following a reset (*RST). Bit
8 CALibration will remain set, however; if the error condition persists.
The Transition Filter The Transition Filter specifies which type of bit transition in the Condition
register will set corresponding bits in the Event register. Transition filter
bits may be set for positive transitions ( 0 to 1), or negative transitions (1 to
0). The commands used to set the transitions are:
STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition <
unmask
>
STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition <
unmask
>
Chapter 3 Understanding the HP E1429 Digitizer 167