IP Addressing
23
Administration for Network Connectivity
555-233-504 — Issue 1 — April 2000 CID: 77730
1 Networking Overview
When to use IP routes
You need to define IP routes only in special cases when default gateways are not
defined or when you want to limit communication between nodes. This section
describes the network configurations that require explicit IP routes.
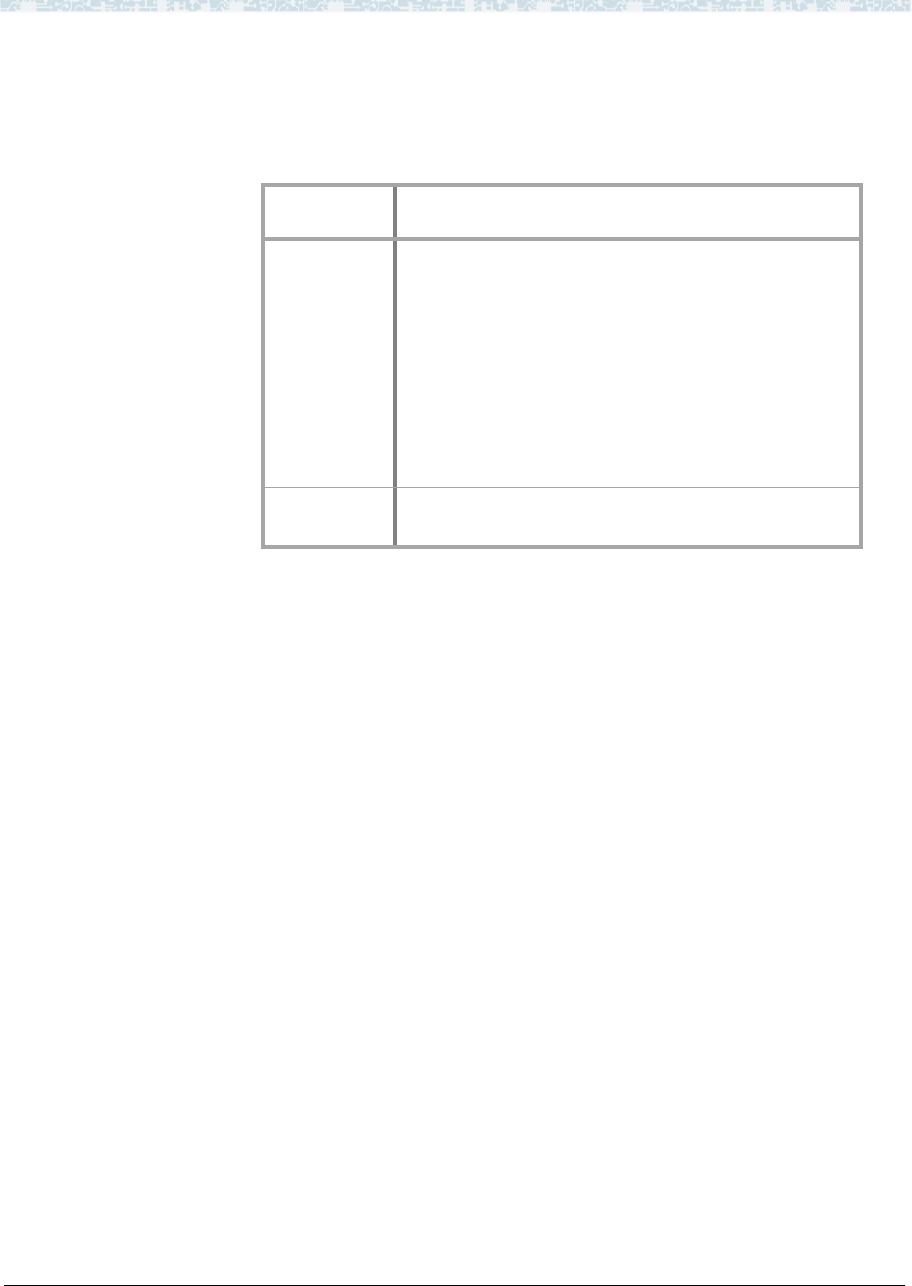
The following table summarizes when you would use IP routes:
The host and network route types are not specified directly. The system implies the
type from the specified destination IP address and its associated subnet mask. The
route type is displayed on the IP Routing screen for the display, list, and modify
commands.
The endpoint nodes are on the same subnet if the following three conditions are met:
• the endpoints are on the same physical subnetwork
• the Subnet Mask field is assigned the same value on the IP Interface
screens for the two endpoint nodes
• the network + subnet portions of the IP addresses (as determined by the
subnet mask) are the same
See Subnetting (page 16) for more information about subnet masks.
Connection
Type
When IP Routes are Needed:
Ethernet
The endpoints are on different subnets and no default
gateway is defined on the IP Interfaces screen for the
local node, and
• You want the local node to communicate with only
the specified node on a remote subnet (this is a
host route type), or
• You want the local node to communicate with any
node a remote network but not with nodes on other
networks (this is a network route type)
PPP
There are one or more intermediate nodes between
endpoints.


















