Managing Device Security
433
ProSafe M5300 Switch
10. Use Max Bandwidth Up to specify the maximum rate (Rate in bits per seconds) at which a
client can send data into the network. 0 indicates to use the global limit (Range: 0 –
536870911 bps.)
11. Use Max Output to specify the number of octets the user is allowed to transmit. After this
limit has been reached the user will be disconnected. 0 indicates to use the global limit
(Range: 0 – 4294967295.)
12. Use Max Input to specify the number of octets the user is allowed to receive. After this limit
has been reached the user will be disconnected. 0 indicates to use the global limit (Range:
0 – 4294967295.)
13. Use Max Total to specify the number of bytes the user is allowed to transmit and receive.
The maximum number of octets is the sum of octets transmitted and received. After this limit
has been reached the user will be disconnected. 0 indicates to use the global limit (Range:
0 – 4294967295.)
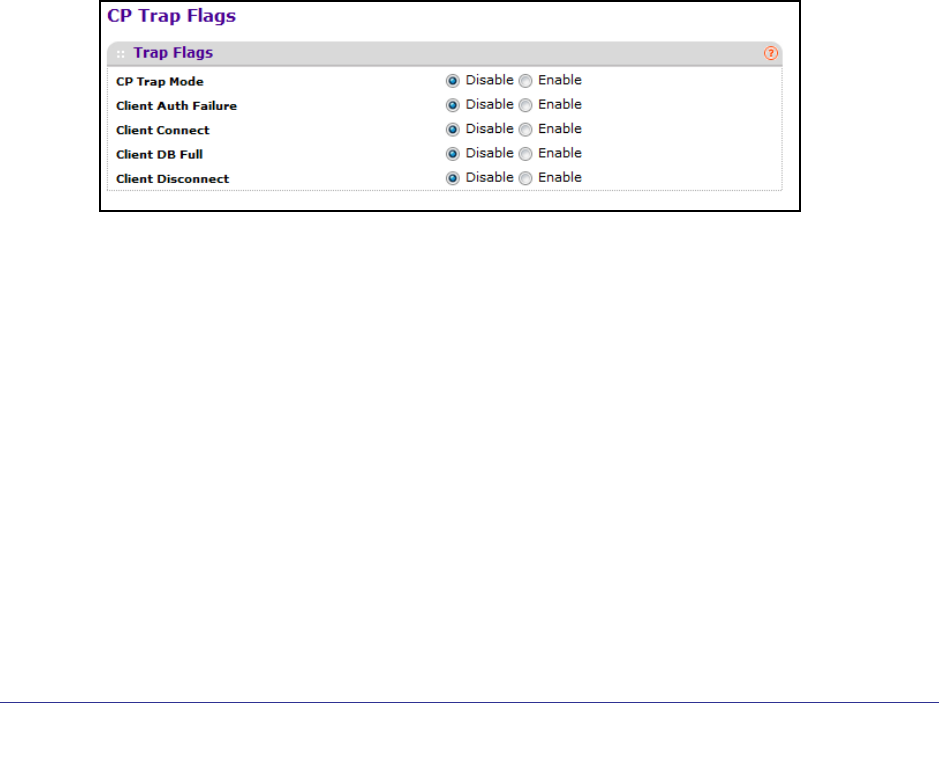
Captive Portal Trap Flags
Use this page to configure whether or not SNMP traps are sent from the Captive Portal and to
specify captive portal events that will generate a trap. All CP SNMP traps are disabled by
default.
To display the Captive Portal Trap Flags page, click Security
Control> Captive Portal CP
Trap Flags.
1. CP Trap Mode - Displays the captive portal trap mode status. To enable or disable the
mode, use the System > SNMP>SNMPv1/v2>Trap Flags page.
2. If you enable the Client Auth Failure field, the SNMP agent sends a trap when a client
attempts to authenticate with a captive portal but is unsuccessful.
3. If you enable the Client Connect field, the SNMP agent sends a trap when a client
authenticates with and connects to a captive portal.
4. If you enable the Client DB Full field, the SNMP agent sends a trap each time an entry
cannot be added to the client database because it is full.
5. If you enable the Client Disconnect field, the SNMP agent sends a trap when a client
disconnects from a captive portal.


















