AMD Geode™ SC2200 Processor Data Book 443
10
Package Specifications 32580B
10.0Package Specifications
10.1 Thermal Characteristics
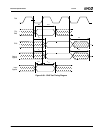
The junction-to-case thermal resistance (θ
JC
) of the pack-
ages shown in Table 10-1
can be used to calculate the
junction (die) temperature under any given circumstance.
Note that there is no specification for maximum junction
temperature given since the operation of the device is
guaranteed to a case temperature range of 0°C to 85°C
(see Table 9-3 on page 370). As long as the case tempera-
ture of the device is maintained within this range, the junc-
tion temperature of the die will also be maintained within its
allowable operating range. However, the die (junction) tem-
perature under a given operating condition can be calcu-
lated by using the following equation:
T
J
= T
C
+ (P * θ
JC
)
where:
T
J
= Junction temperature (°C)
T
C
= Case temperature at top center of package (°C)
P = Maximum power dissipation (W)
θ
JC
= Junction-to-case thermal resistance (°C/W)
These examples are given for reference only. The actual
value used for maximum power (P) and ambient tempera-
ture (T
A
) is determined by the system designer based on
system configuration, extremes of the operating environ-
ment, and whether active thermal management (via Sus-
pend Modulation) of the GX1 module is employed.
A maximum junction temperature is not specified since a
maximum case temperature is. Therefore, the following
equation can be used to calculate the maximum thermal
resistance required of the thermal solution for a given max-
imum ambient temperature:
where:
θ
CS
= Max case-to-heatsink thermal resistance (°C/W)
allowed for thermal solution
θ
SA
= Max heatsink-to-ambient thermal resistance (°C/W)
allowed for thermal solution
T
A
= Max ambient temperature (°C)
T
C
= Max case temperature at top center of package (°C)
P = Maximum power dissipation (W)
If thermal grease is used between the case and heatsink,
θ
CS
will reduce to about 0.01 °C/W. Therefore, the above
equation can be simplified to:
where:
θ
CA
= θ
SA
= Max heatsink-to-ambient thermal resistance
(°C/W) allowed for thermal solution
The calculated θ
CA
value (examples shown in Table 10-2)
represents the maximum allowed thermal resistance of the
selected cooling solution which is required to maintain the
maximum T
CASE
(shown in Table 9-3 on page 370) for the
application in which the device is used.
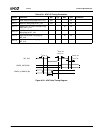
Table 10-1. θ
JC
(×C/W)
Package Max (°C/W)
BGU481 5
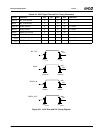
θ
CS
+ θ
SA
=
T
C
− T
A
P
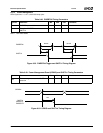
θ
CA
=
T
C
− T
A
P
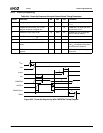
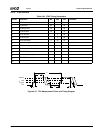
Table 10-2. Case-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance Example @ 85°C
Core Voltage
(V
CORE
)
(Nominal)
Core
Frequency
Maximum
Power (W)
θ
CA
for Different Ambient Temperatures (°C/W)
20°C25°C30°C35°C40°C
1.8V 266 MHz 3.32 19.58 18.07 16.57 15.06 13.55