Interrupts
Description
MN102H75K/F75K/85K/F85K LSI User Manual Panasonic Semiconductor Development Company
37
Panasonic
2 Interrupts
2.1 Description
The most important factor in real-time control is an MCU’s speed in servicing
interrupts. The MN102H75K/85K has an extremely fast interrupt response time
due to its ability to abort instructions, such as multiply or divide, that require
multiple clock cycles. The MN102H75K/85K re-executes an aborted instruction
after returning from the interrupt service routine.
This section describes the interrupt system in the MN102H75K/85K. The
MN102H75K/85K contains 36 interrupt group controllers. Each controls a single
interrupt group. Because each group contains only one interrupt vector, the
MN102H75K/85K can handle interrupts much quicker than previously possible.
Each interrupt group belongs to one of twelve classes, which defines its interrupt
priority level.
With the exception of reset interrupts, all interrupts from timers, other peripheral
circuits, and external pins must be registered in an interrupt group controller.
Once they are registered, interrupt requests are sent to the CPU in accordance
with the interrupt mask level (0 to 6) set in the interrupt group controller. Groups
1 to 3 are dedicated to system interrupts. Table 2-1 compares the interrupt
parameters of the MN102H75K/85K to those of the MN102L35G, the com-
parable MCU in the previous generation of the 16-bit series.
The MN102H75K/85K has six external interrupt pins. Set the interrupt condition
(positive edge, negative edge, either edge, or active low) in the EXTMD register.
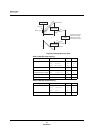
Table 2-1 Comparison of MN102H75K/85K and MN102L35G Interrupt Features
Parameter MN102L35G MN102H75K/85K
Interrupt groups
(IAGR group numbers
4 vectors per group
(Separated by interrupt
service routine)
1 vector per group
(Group number gener-
ated for each interrupt)
Interrupt response time Good Excellent
Interrupt level settings 4 vectors per level 4 vectors per level
Software compatibility — Easily modified
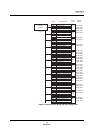
Figure 2-1 Interrupt Controller Block Diagram
IRQ0
IRQ1
IRQ2
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
Edge/level
Edge/level
Edge/level
Edge/level
Edge/level
Edge/level
EXTMD
Interrupt
arbitration
.
.
.
.
.
.
Internal
interrupts
Interrupt
to CPU