Page 9-18
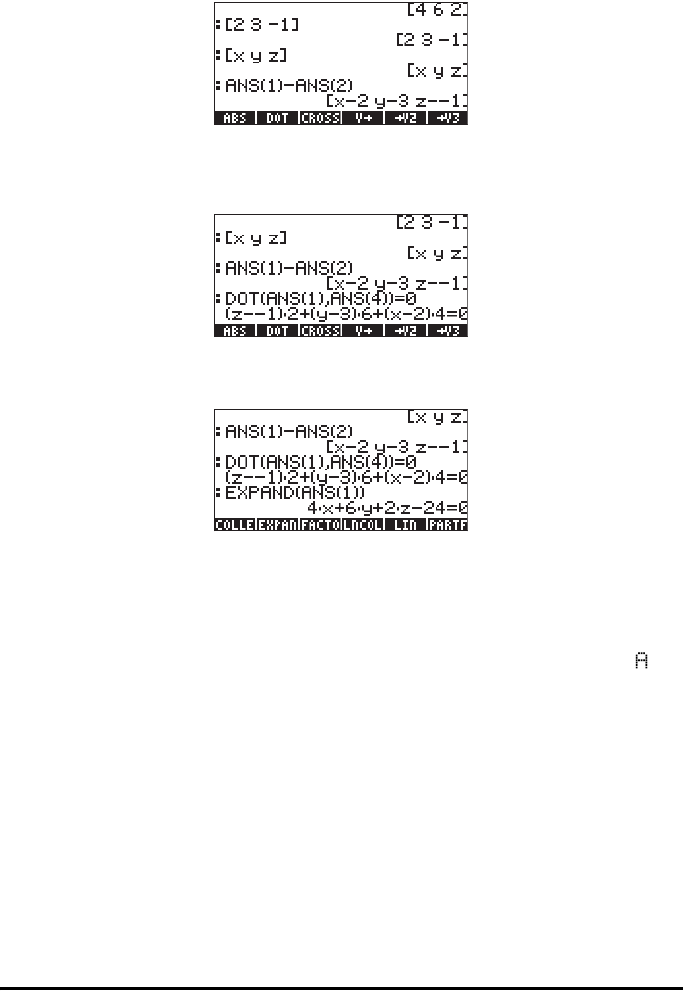
Next, we calculate vector P
0
P = r as ANS(1) – ANS(2), i.e.,
Finally, we take the dot product of ANS(1) and ANS(4) and make it equal to
zero to complete the operation N•r =0:
We can now use function EXPAND (in the ALG menu) to expand this
expression:
Thus, the equation of the plane through point P
0
(2,3,-1) and having normal
vector N = 4i+6j+2k, is 4x + 6y + 2z – 24 = 0. In RPN mode, use:
[2,3,-1] ` ['x','y','z'] ` - [4,6,2] DOT EXP ND
Row vectors, column vectors, and lists
The vectors presented in this chapter are all row vectors. In some instances, it is
necessary to create a column vector (e.g., to use the pre-defined statistical
functions in the calculator). The simplest way to enter a column vector is by
enclosing each vector element within brackets, all contained within an external
set of brackets. For example, enter:
[[1.2],[2.5],[3.2],[4.5],[6.2]] `
This is represented as the following column vector:





















