Page 2-3
Binary integers, objects of type 10, are used in some computer science
applications.
Graphics objects, objects of type 11, store graphics produced by the calculator.
Tagged objects, objects of type 12, are used in the output of many programs to
identify results. For example, in the tagged object:
Mean: 23.2, the word Mean:
is the tag used to identify the number
23.2 as the mean of a sample, for
example.
Unit objects, objects of type 13, are numerical values with a physical unit
attached to them.
Directories, objects of type 15, are memory locations used to organize your
variables in a similar fashion as folders are used in a personal computer.
Libraries, objects of type 16, are programs residing in memory ports that are
accessible within any directory (or sub-directory) in your calculator. They
resemble built-in functions, objects of type 18, and built-in commands, objects
of type 19, in the way they are used.
Editing expressions on the screen
In this section we present examples of expression editing directly into the
calculator display (algebraic history or RPN stack).
Creating arithmetic expressions
For this example, we select the Algebraic operating mode and select a Fix
format with 3 decimals for the display. We are going to enter the arithmetic
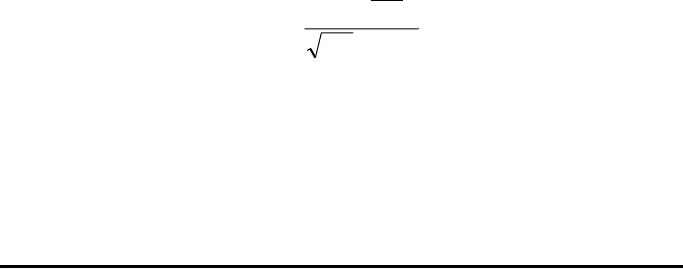
expression:
To enter this expression use the following keystrokes:
5.*„Ü1.+1./7.5™/
„ÜR3.-2.Q3
3
0.20.3
5.7
0.1
0.1
0.5
−
+
⋅


















