Page 18-8
to calculate for uniform-size classes (or bins), and the class mark is just the
average of the class boundaries for each class. Finally, the cumulative
frequency is obtained by adding to each value in the last column, except the
first, the frequency in the next row, and replacing the result in the last column of
the next row. Thus, for the second class, the cumulative frequency is 18+15 =
33, while for class number 3, the cumulative frequency is 33 + 16 = 49, and so
on. The cumulative frequency represents the frequency of those numbers that
are smaller than or equal to the upper boundary of any given class.
Given the (column) vector of frequencies generated by the calculator, you can
obtain a cumulative frequency vector by using the following program in RPN
mode:
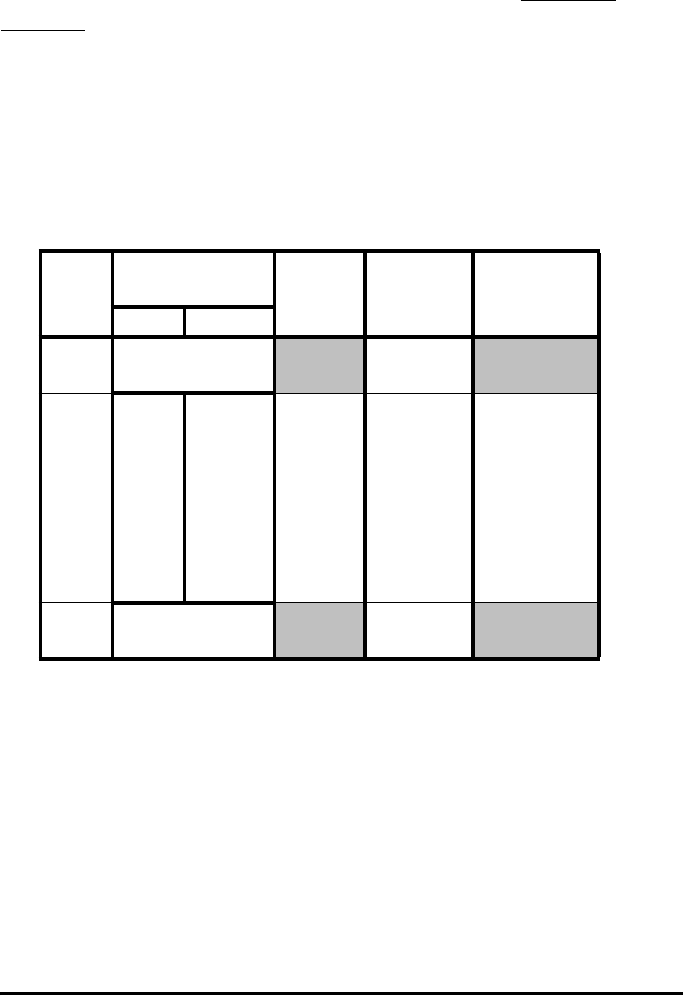
Class
No.
Class Bound. Class
mark.
Frequency Cumulative
iXB
i
XB
i+1
Xm
i
f
i
frequency
< XB
1
outlier below
range
25
11020 15 18 18
220 30 25 14 32
33040 35 17 49
44050 45 17 66
55060 55 22 88
660 70 65 22 110
770 80 75 24 134
k = 8 80 90 85 19 153
>XB
k
outliers above
range
22


















