Intel® 460GX Chipset Software Developer’s Manual 7-13
AGP Subsystem
7.2.7.11 Fast Back-to-Back Transactions
The GXB as a PCI target will accept fast back-to-back cycles from a PCI master accessing different
agents during back-to-back sequence. As an initiator the GXB does not generate a fast back-to-
back cycle.
7.3 Bandwidth
The bandwidth of AGP 4X mode is 1 GB peak. The sustained bandwidth will be less than this. The
sustainable bandwidth obtainable with the GX is dependent on several things including the size of
the requests from the graphics card. Table 7-5 shows an estimate of obtainable bandwidth. There is
a fairly broad range for each of the sizes. The bandwidth will depend on the mix of traffic. Traffic
consisting of all reads by the graphics card or all writes by the processor to the card will result in
higher bandwidths than a 50/50 mix of reads by the graphics card and writes by the processor to the
card. This table will change as the implementation is completed and should be viewed as a
guideline for the graphics card designer for relative performance trade-offs.
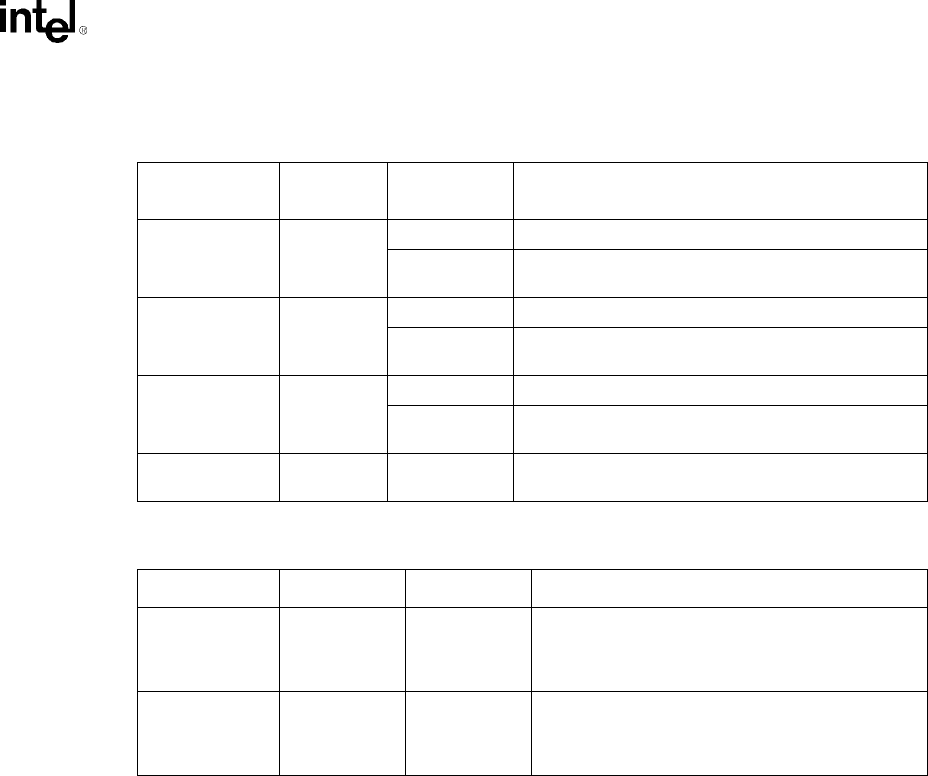
Table 7-3. Burst Write Combining Modes
Write Command
Used
Transfer
Mode
Data Length Combining Supported
Memory Write 1X < 4 DW Can not be combined with the next access.
>= 4 DW Can combine next access if it is sequential, regardless
of next access size.
Memory Write 2X < 8 DW Can not be combined with the next access.
>= 8 DW Can combine next access if it is sequential, regardless
of next access size.
Memory Write 4X < 16 DW Can not be combined with the next access.
>= 16 DW Can combine next access if it is sequential, regardless
of next access size.
Memory Write
Invalidate
All must be Line Can only combine sequential lines.
Table 7-4. Burst Write Combining Examples with 3 Writes in 1X Transfer Mode
1st write 2nd write 3rd write Transferred as:
x DW
(x<4)
y DW z DW if y < 4
x DW followed by y DW followed by z DW
else
x DW followed by (y+z) DW
x DW
(x>=4)
y DW z DW if y < 4
(x+y) DW followed by z DW
else
(x+y+z) DW