- 690 -
11.2.15 Defining DNS Relay Function
11.2.15.1 Configuring DNS Relay Configuration Page
The DNS protocol controls the Domain Name System (DNS), a distributed database with which you can
map host names to IP addresses. When you configure DNS on your switch, you can substitute the host
name for the IP address with all IP commands, such as ping, telnet, traceroute, and related Telnet support
operations. To keep track of domain names, IP has defined the concept of a domain name server, which
holds a cache (or database) of names mapped to IP addresses. To map domain names to IP addresses,
you must first identify the host names, specify the name server that is present on your network, and
enable the DNS.
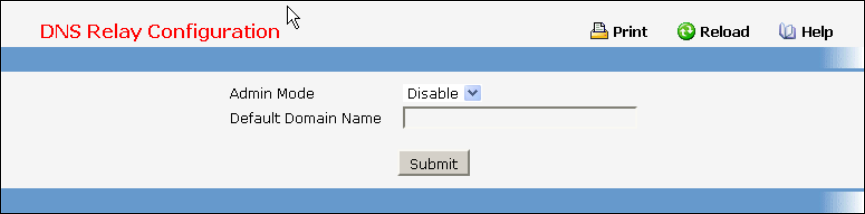
Selection Criteria
Admin Mode - Select enable or disable from the pull down menu. When you select 'enable', the IP
Domain Naming System (DNS)-based host name-to-address translation will be enabled.
Configurable Data
Default Domain Name - Default domain name used to complete unqualified host names. Do not
include the initial period that separates an unqualified name from the domain name. This is a text
string of up to 63 characters.
Command Buttons
Submit - Send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take effect
immediately. These changes will not be retained across a power cycle unless a save is performed.
11.2.15.2 Configuring Domain Name Configuration Page
You can use this screen to change the configuration parameters for the domain names that can be
appended to incomplete host names (i.e., host names passed from a client that are not formatted with
dotted notation). You can also use this screen to display the contents of the table.


















