- 796 -
LSAs Received - The number of LSAs (link state advertisements) received that were determined to
be new instantiations. This number does not include newer instantiations of self-originated LSAs.
Command Buttons
Submit - Send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take effect
immediately. These changes will not be retained across a power cycle unless a save is performed.
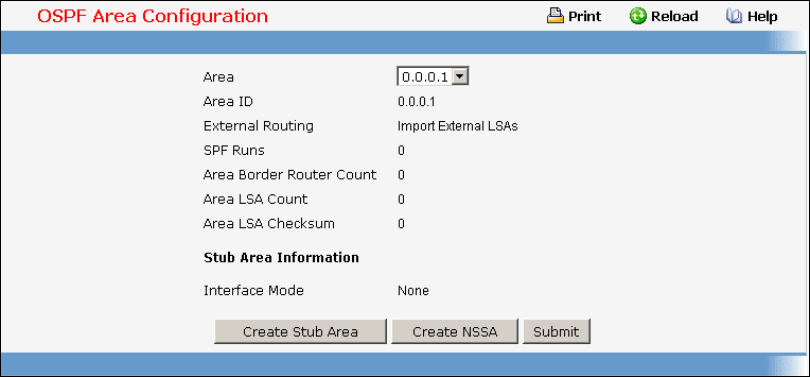
11.4.3.2 Configuring Area
Configurable Data
Router ID - The 32 bit integer in dotted decimal format that uniquely identifies the router within the
OSPF domain. If you want to change the Router ID you must first disable OSPF. After you set the new
Router ID, you must re-enable OSPF to have the change take effect. The default value is 0.0.0.0,
although this is not a valid Router ID.
OSPF Admin Mode - Select Enable or Disable from the pulldown menu. If you select Enable OSPF
will be activated for the switch. The default value is Enable. You must configure a Router ID before
OSPF can become operational.
RFC 1583 Compatibility - Select Enable or Disable from the pulldown menu to specify the
preference rules that will be used when choosing among multiple AS-external-LSAs advertising the
same destination. If you select Enable, the preference rules will be those defined by RFC 1583. If you
select Disable, the preference rules will be those defined in Section 16.4.1 of RFC 2328. The newer
preference rules prevent routing loops when AS-external-LSAs for the same destination have been
originated from different areas. The default value is Enable. All routers in the OSPF domain must be
configured the same. If all OSPF routers are capable of operating according to RFC 2328, RFC 1583
Compatibility should be disabled.
Opaque LSA Status - Set this parameter to Enable to if OSPF should store and flood opaque LSAs.
An opaque LSA is used for flooding user-defined information within an OSPF router domain.
Exit Overflow Interval - When the number of non-default external LSAs exceeds a configured limit,
the router enters an overflow state as defined in RFC 1765. The Exit Overflow Interval specifies how
long OSPF must wait before attempting to leave overflow state. In overflow state, OSPF cannot
originate non-default external LSAs. If the Exit Overflow Interval is 0, OSPF will not leave overflow
state until it is disabled and re-enabled. The range is 0 to 2,147,483,647 seconds.


















