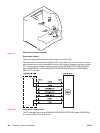
● Print temperature control: Maintains the fuser heater in the printer at the target
temperature. The CPU raises the target temperature in stages in one sprinting process
to prevent the fuser sleeve temperature from falling as the paper goes through. During
printing of multiple pages, the target temperature also varies in stages depending on the
number of pages printed.
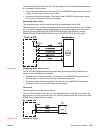
● Between-sheets temperature control: Keeps the temperature of the fuser heater lower
than the target temperature during continuous printing. This prevents the temperature
rise of the fuser sleeve between sheets. The between-sheets temperature varies
depending on the paper feed speed and the kind of paper being printed.
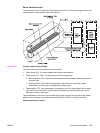
● Throughput control: Prevents both ends of the fuser sleeve unit from overheating during
continuous printing of narrow paper. For continuous printing, this control decreases the
throughput to slow down the paper pickup speed when the temperature of the sub
thermistor reads over 260˚ C (500˚ F) and the paper width is narrower than 210 mm
(8.27 inches).
Flicker prevention
The flicker prevention mechanism prevents flicker when the user’s printer is connected to the
same AC line as other lighting fixtures. Because the printer’s heater drive circuit uses a triac
for switching AC, flicker can occur when the voltage in the AC line falls due to a user
connecting a printer to the same AC line as other lighting fixtures, increasing the amount of
current passing through the heater.
To prevent flicker, this printer uses a zero crossing circuit to monitor the voltage of the AC
line. The CPU monitors the ZERO CROSSING DETECTION signal (ZEROX) to optimize the
timing of energizing the heater.
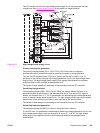
Protective function
The CPU, fuser heater safety circuit, and thermoswitch prevent overheating of the fuser by
interrupting the current to the heater.
The abnormal temperature rise is prevented by the following parts:
1. CPU
2. Fuser heater safety circuit
3. Thermoswitch
The function of each part is described as follows:
● CPU: The CPU monitors the output voltages of the main and sub thermistors (MAINTH,
SUBTH). If the MAINTH voltage goes below approximately 0.92 V (230˚ C, 446˚ F) or
the SUBTH voltage exceeds approximately 2.8 V (280˚ C, 536˚ F), the CPU judges the
fuser faulty and initiates the following steps.
● The CPU sets the FUSER HEATER DRIVE signal (FSRD) to stop “L” via ASIC and
turns off the heater.
● The CPU sets the RELAY DRIVE signal (RLD) to stop (“H”).
● The fuser heater safety circuit turns the RELAY DRIVE signal (RLD-) to stop (“H”).
● The relay drive circuit cuts the relay (RL301) OFF and interrupts the current to the
fuser heater.
● Fuser heater safety circuit: The CPU monitors the output voltages of the main and sub
thermistors (MAINTH and SUBTH). It cuts the relay (RL301) off and interrupts the
current to the fuser heater when the MAINTH voltage is under approximately 1.0 V (240˚
C, 464˚ F) or the SUBTH voltage exceeds approximately 3.0 V (290˚ C, 554˚ F).
● Thermoswitch: When the thermoswitch reads a temperature exceeding 250˚ C (482˚ F),
it is disconnected, interrupting the current to the fuser heater.
ENWW Engine control system 129