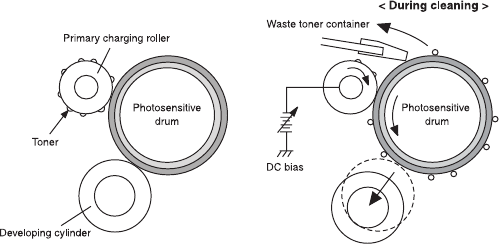
The DC controller disengages the developing cylinder to start this control and apply two
negative biases alternately to the primary charging roller. This attracts the toner away from
the primary charging roller to the photosensitive drum. The toner on the photosensitive drum
is then scraped off the drum by the cleaning blade to be delivered to the waste toner
container.
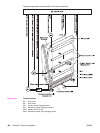
Figure 5-43.
Transfer section diagram
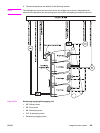
Transfer section
The transfer section, see the figure on the following page, consists of the transfer unit and
the secondary transfer unit. The transfer unit transfers the toner on the photosensitive drum
to the ITB. The secondary transfer unit then transfers the toner on the ITB to the paper.
ITB (transfer) unit
The ITB unit consists of components such as ITB, primary transfer roller, ITB feed roller, and
waste toner full sensor.
As the drum motor (M3) rotates the ITB feed roller, the ITB feed roller rotates the ITB, and
the ITB rotates the primary transfer roller.
The primary transfer roller engaging cam is to engage or disengage the Y, M, and C
cartridge’s primary transfer rollers from the ITB. It is rotated by the primary transfer roller
engaging motor (M5).
The waste toner full sensor detects whether the toner piled up in the waste toner container if
full after the ITB cleaning.
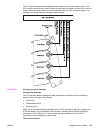
Secondary transfer unit
The secondary transfer unit consists of components, such as the secondary transfer roller,
secondary transfer roller engaging cam, and secondary transfer engaging sensor.
The secondary transfer roller transfers the toner on the ITB to the paper. It is interlocked with
the ITB. The secondary transfer roller engaging cam is to engage or disengage the
secondary transfer roller from the ITB. It is rotated by the delivery motor (M1) as the
secondary transfer roller engaging solenoid (SL4) opens or closes.
The secondary transfer roller engaging sensor monitors whether or not the roller is engaged
with the ITB.
The transfer section performs the following:
164 Chapter 5 Theory of operation ENWW