10--------...---
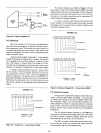
MEMR
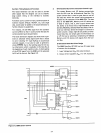
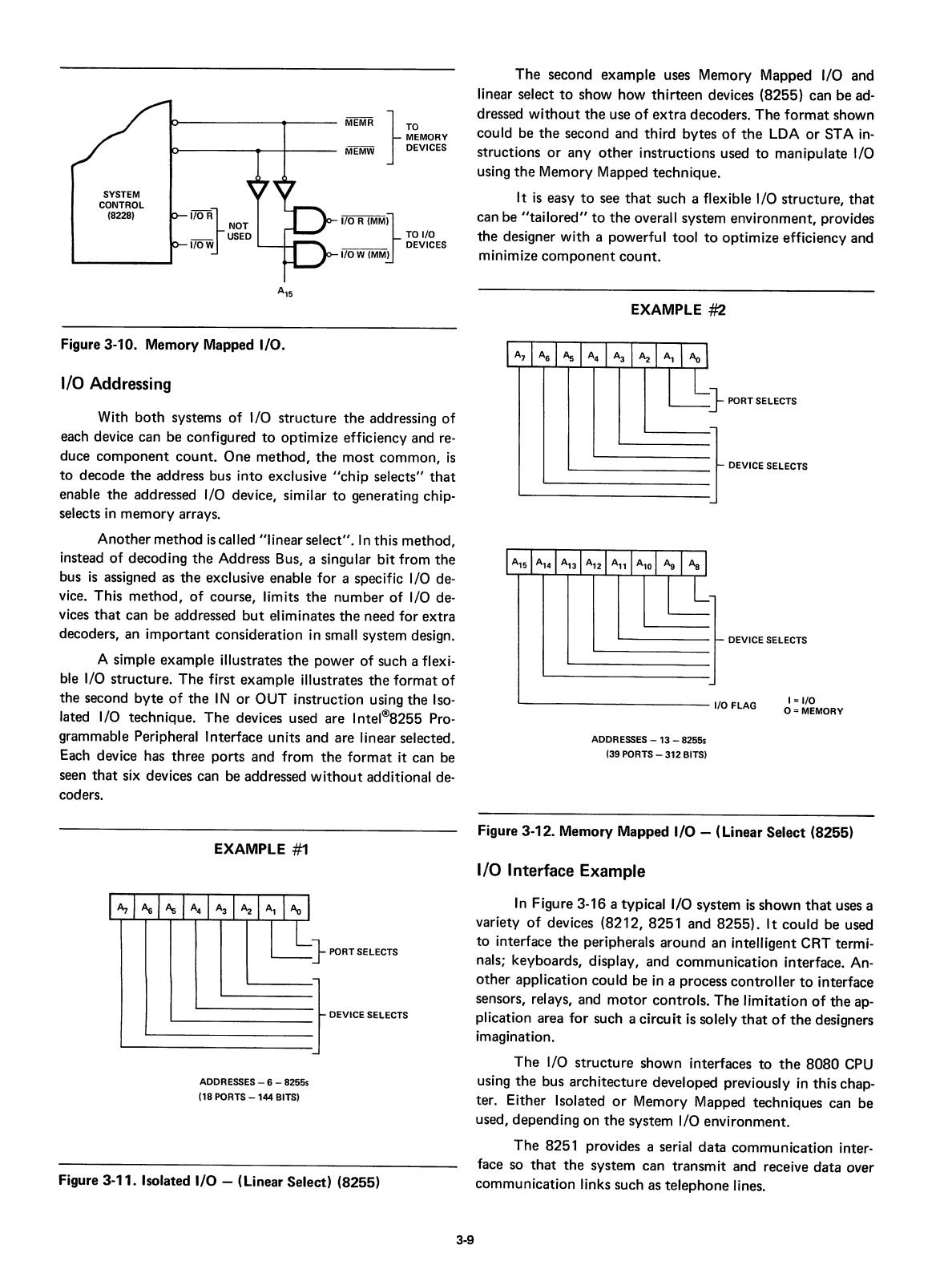
The
second
example
uses Memory Mapped I/O and
linear select
to
show how
thirteen
devices (8255) can
be
ad-
dressed
without
the
use
of
extra
decoders.
The
format
shown
could be
the
second and third bytes
of
the
LDA
or
STA
in-
structions
or
any
other
instructions used
to
manipulate
I/O
using
the
Memory Mapped
technique.
It
is
easy
to
see
that
such a flexible I/O
structure,
that
can be
"tailored"
to
the
overall system environment, provides
the
designer
with
a powerful tool
to
optimize
efficiency and
minimize
component
count.
}
TO
MEMORY
DEVICES
I/O R
(MMJ-
TO I/O
DEVICES
I/OW
(MM)
I/OR}
NOT
_
USED
IIOW
r>-----.---+----
MEMW
SYSTEM
CONTROL
(8228)
EXAMPLE
#2
} PORTSELECTS
'--
}
DEVICE
SELECTS
"'------------
1/0 FLAG
I =I/O
0=
MEMORY
DEVICE SELECTS
ADDRESSES
-13
- 82555
(39
PORTS
- 312BITS)
I/O Addressing
With
both
systems
of
I/O
structure
the
addressing
of
each device can be configured
to
optimize
efficiency and re-
duce
component
count.
One
method,
the
most
common,
is
to
decode
the
address bus
into
exclusive
"chip
selects"
that
enable
the
addressed I/O device, similar
to
generating chip-
selects
in
memory
arrays.
Another
method
is
called "Iinear
select".
In
this
method,
instead
of
decoding
the
Address Bus, a singular
bit
from
the
bus
is
assigned as
the
exclusive enable for a specific I
/0
de-
vice. This
method,
of
course, limits
the
number
of
I/O de-
vices
that
can
be
addressed
but
eliminates
the
need for
extra
decoders, an
important
consideration in small system design.
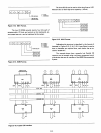
A simple example illustrates
the
power
of
such a flexi-
ble I/O structure.
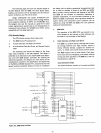
The
first example illustrates
the
format
of
the
second
byte
of
the
IN
or
0 UT instruction u
si
ng
the
Iso-
lated I/O technique.
The
devices used are Intel®8255 Pro-
grammable Peripheral Interface
units
and are linear selected.
Each device has
three
ports
and from
the
format
it can be
seen
that
six devices can be addressed
without
additional de-
coders.
Figure 3-10. Memory Mapped
I/O.
Figure 3-12. Memory Mapped
I/O
- (Linear Select (8255)
EXAMPLE
#1
I/O
Interface Example
} PORT SELECTS
'--
}
DEVICE
SELECTS
ADDRESSES - 6 - 82555
(18 PORTS
-144
BITS)
Figure 3-11. Isolated
I/O
- (Linear Select) (8255)
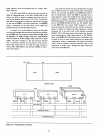
In
Figure 3-16 a typical I/O system
is
shown
that
uses a
variety
of
devices (8212, 8251 and
8255).
It
could
be used
to
interface
the
peripherals
around
an intelligent CRT termi-
nals; keyboards, display, and
communication
interface. An-
other
application could be
in
a process
controller
to
interface
sensors, relays, and
motor
controls.
The
limitation
of
the
ap-
plication area
for
such a
circuit
is solely
that
of
the
designers
imagination.
The
I/O
structure
shown interfaces
to
the
8080
CPU
using
the
bus
architecture
developed previously
in
this chap-
ter. Either Isolated
or
Memory Mapped
techniques
can be
used, depending on
the
system I/O environment.
The
8251 provides a serial
data
communication
inter-
face so
that
the
system can transmit and receive
data
over
communication links such as
telephone
lines.
3-9