intel®
Silicon Gate MOS
8080
A
SINGLE CHIP a-BIT N-CHANNEL MICROPROCESSOR
The 8080A
is
functionally and electrically compatible with the Intel® 8080.
• TTL Drive Capability
• 2
J.Ls
Instruction Cycle
• Powerful Problem Solving
Instruction Set
• Six General Purpose Registers
and an Accumulator
• Sixteen Bit Program Counter for
Directly Addressing up to 64K Bytes
of Memory
• Sixteen Bit Stack Pointer and Stack
Manipulation Instructions for Rapid
Switching of the Program Environment
• Decimal,Binary and Double
Precision Arithmetic
• Ability to Provide Priority Vectored
Interrupts
• 512 Directly Addressed
I/O
Ports
The
Intel®
8080A
is
a
complete
8-bit parallel central processing
unit
(CPU). It
is
fabricated
on
a single
LSI
chip
using Intel's
n-channel silicon gate
MOS
process. This offers
the
user a high performance solution
to
control and processing applications.
The
8080A
contains six 8-bit general purpose working registers and an accumulator.
The
six general purpose registers may be
addressed individually
or
in
pairs providing
both
single and double precision operators.
Arithmetic
and logical instructions
set
or
reset four testable flags. A fifth flag provides decimal arithmetic operation.
The
8080A has an external stack feature wherein any portion
of
memory may be used as a last in/first
out
stack
to
store/
retrieve
the
contents
of
the
accumulator, flags, program
counter
and
all
of
the
six general purpose registers.
The
sixteen
bit
stack pointer controls
the
addressing
of
this
external stack. This stack gives
the
8080A
the
ability
to
easily handle multiple
level priority interrupts
by
rapidly storing and restoring processor status. It also provides almost unlimited
subroutine
nesting.
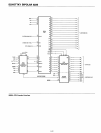
This microprocessor has been designed
to
simplify systems design. Separate 16-line address and 8-line bi-directional
data
busses are used
to
facilitate easy interface
to
memory and I/O. Signals
to
control
the
interface
to
memory
and I/O are pro-
vided directly
by
the
8080A.
Ultimate control
of
the
address and
data
busses resides
with
the
HOLD signal. It provides
the
ability
to
suspend processor
operation
and force
the
address and
data
busses into a high impedance state. This permits OR-
tying these busses with
other
controlling devices
for
(DMA) direct memory access
or
mUlti-processor operation.
:.,.
;
.
:',
".
..
,
.
...
.,.
:/
",',"
:·i.'
,<'.,
<:
:::.
·:i··.
:,
.
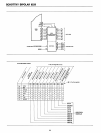
W
(8)
Z
(8)
TEMP REG.
TEMP REG.
B
(8)
C
(8)
REG.
REG.
D
(8)
E
(8)
REG.
REG.
H
(8)
L
(8)
'\'
REG.
REG.
STACK POINTER
(16)
(16)
PROGRAM COUNTER
.:
..
TIMING
.
'.'
...
,:
:'>;
'/:;):".,
:;:",
':
~',:,
'.;:':'
;
,.'H:.:
':~,
•.
'
."
'.o;?oo .'H.;
>::....
c·...
'<1:,:
,:
,'.
:
.•..
'.:.:
.
~:?
:.
:
..
...•
:'..':.
't
.;.
;)it~:'
'';','':
;;:"'.,.':':J
:
....
::;."
..
>:.~
.;
..
r·:
ACCUMULATOR
:....
(8)
./:,
<~'>:'.~
ACCUMULATOR
.-,;
LATCH
(8)
.~
5-13