391
B.3 Bit Manipulation Instructions (SETB and CLRB)
Some registers of peripheral functions have bits that perform a read operation different
from ordinary read for a bit manipulation instruction.
■ Read-modify-write Operation
The bit manipulation instructions can set "1" (SETB) to the specified bit in a register or RAM or clear it to
"0" (CLRB). Because the CPU handles the data in 8 bits, however, it actually reads the 8-bit data, modifies
the specified bit, and then writes it back to the original address. This series of operations is called read-
modify-write operation.
Table B.3-1 shows the bus operation at bit manipulation instructions.
■
Read Destination at Execution of a Bit Manipulation Instruction
For some I/O ports and interrupt request flag bits, the read destination for read-modify-write is different
from that for ordinary read.
● I/O port (at bit manipulation)
For some I/O ports, the value of the I/O pin is read at ordinary read; meanwhile, the value of output latch is
read at bit manipulation. This is to prevent the other bits of the output latch from being accidentally
changed regardless of the I/O direction and pin state.
● Interrupt request flag bit (at bit manipulation)
The interrupt request flag bits work as flag bits for confirming an interrupt request at ordinary read;
meanwhile, "1" is always read at bit manipulation. This is to prevent the interrupt request flag bits from
being written as "0", and accidentally clearing the flags at bit manipulation for another bit.
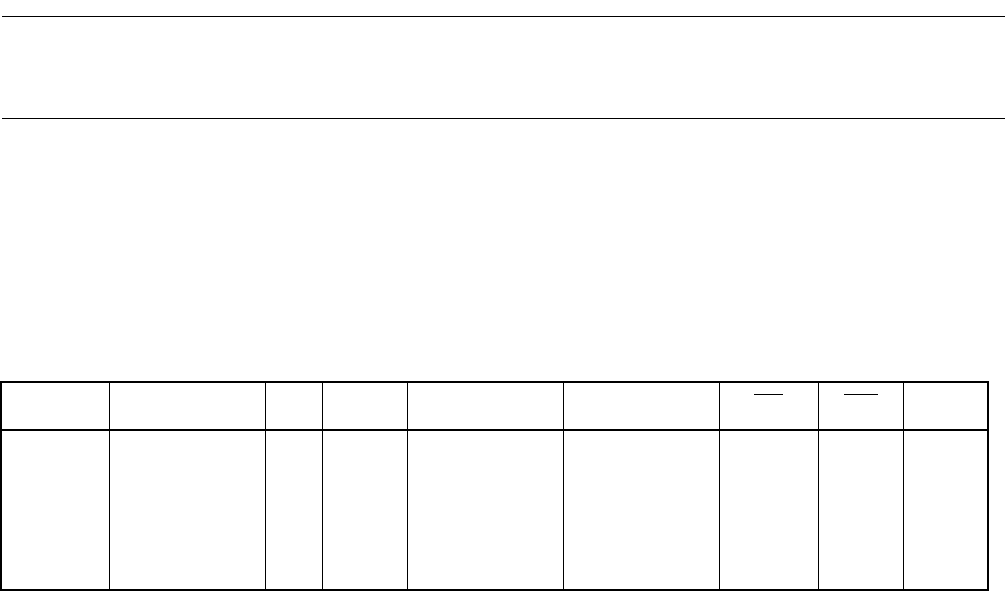
Table B.3-1 Bus Operation at Bit Manipulation Instructions
CODE MNEMONIC ~ Cycle Address bus Data bus RD
WR RMW
A0 to A7 CLRB dir:b 4 1 N+1 Dir 0 1 0
2 dir address Data 0 1 1
A8 to AF SETB dir:b 3 dir address Data 1 0 0
4 N+2 Next operation 0 1 0


















