e-STUDIO3511/4511 COPY PROCESS 3 - 2 November 2003 © TOSHIBA TEC
3
2
3
7
4
5-2
8
5-1
1
9
10
6
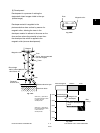
Original exposure
Xenon lamp
16 W
Data reading (scanning)
CCD
600dpi, 7450 pixels
Image processing
Data writing
Semiconductor laser
Pw=4.0 nJ/mm
2
Discharging (LED array)
Wavelength 660nm x 14pcs.
Charger (grid voltage)
Cleaning
-1000 V
Fusing
IH coil
700 to 1300 W
Paper exit
2nd transfer
(+)1000V (500 to 4800V)
(-)-1000V (-100 to –2000V)
Bypass feeding
PFP/LCF feeding
Drawer feeding
Color development
Magnetic roller bias
-400V (-100 to -900V) DC
1.0 kV/10kHz AC
Carrier
Toner
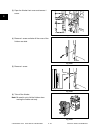
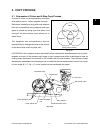
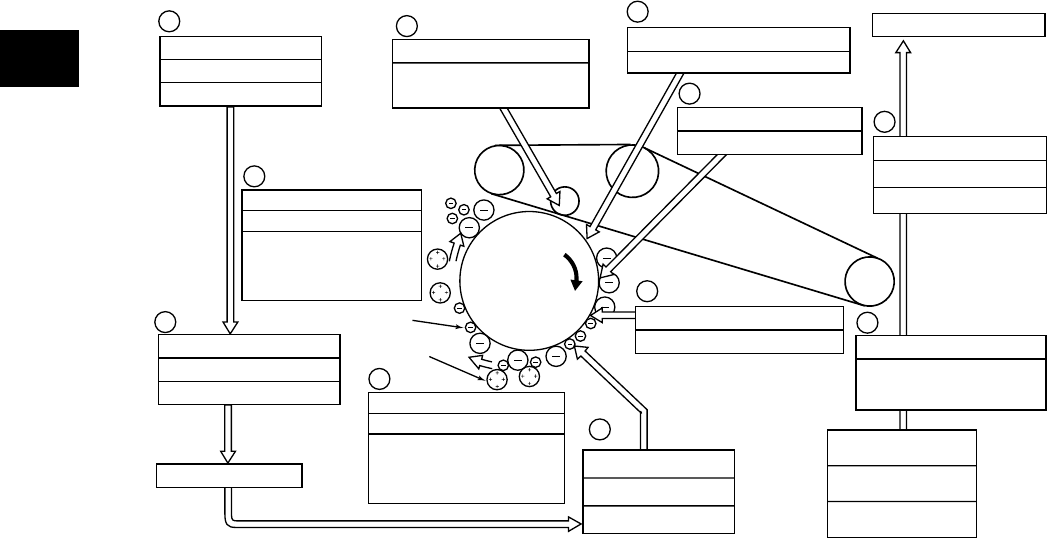
3.2 General Description of Copying Process
1. Charging: Places a negative charge on the
surface of the photoconductive drum.
↓
2. Original exposure: Converts images on the
original into optical signals.
↓
3. Data reading: The optical image signals are
read into CCD and converted into electrical
signals.
↓
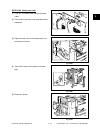
4. Data writing: The electrical image signals are
changed to light signals (by laser emission)
which expose the surface of the
photoconductive drum.
↓
5. Development: Negatively-charged toner is
made to adhere to the photoconductive drum,
producing a visible image.
↓
6. 1st transfer: Transfers the visible image
(toner) on photoconductive drum to the
transfer belt.
↓
7. 2nd transfer: Transfers the visible image
(toner) on the transfer belt to paper.
↓
8. Fusing: Fuses the toner image to the paper
by applying heat and pressure.
↓
9. Blade cleaning : While scraping off the
residual toner from the drum by the blade,
this blade also eliminates the (+) residual
charge on the drum left after image transfer.
↓
10. Discharging: Eliminates the residual (–)
charge from the surface of the
photoconductive drum.
Photocon-
ductive drum
1800V (400 to 4000V)
1st transfer
Black development
Magnetic roller bias
-400V (-100 to -900V) DC
1.2 kV/10kHz AC
-600V (-300 to -1200V)
Fig. 3-201
04/01