Calibration and Verification
Calibrating the 5700A/5720A Series II to External Standards
3
3-7
3-7. Calibration Requirements
Both the calibrator and the recommended external standards have the ability to internally
control (or compensate for) ambient temperature variations. Therefore it is unnecessary
to keep the calibrator in tightly controlled temperatures during calibration. During the
calibration procedure, the calibrator prompts you to enter the ambient temperature, and
includes this information in specification readouts and output shift reports.
3-8. When to Adjust the Calibrator’s Uncertainty Specifications
Table 3-1 lists each external standard’s uncertainty limit, and the 5700A/5720A Series II
uncertainty specifications that must adjusted accordingly if that limit is exceeded.
As long as the external standards have the uncertainties listed in Table 3-1, you do not
need to adjust the calibrator’s absolute uncertainty specifications in Chapter 1. However,
if your standard’s uncertainty exceeds the value in the table you must adjust some of the
calibrator’s absolute uncertainty specifications by the algebraic difference between your
standard’s uncertainty and the uncertainty limit listed in the Table 3-1. For example, if
the dc voltage standard has an uncertainty of ±2.5 ppm, then the 5700A and the 5720A
absolute uncertainty specifications listed in Table 3-1 for the traceable quantity of
voltage must all be increased by ±1 ppm.
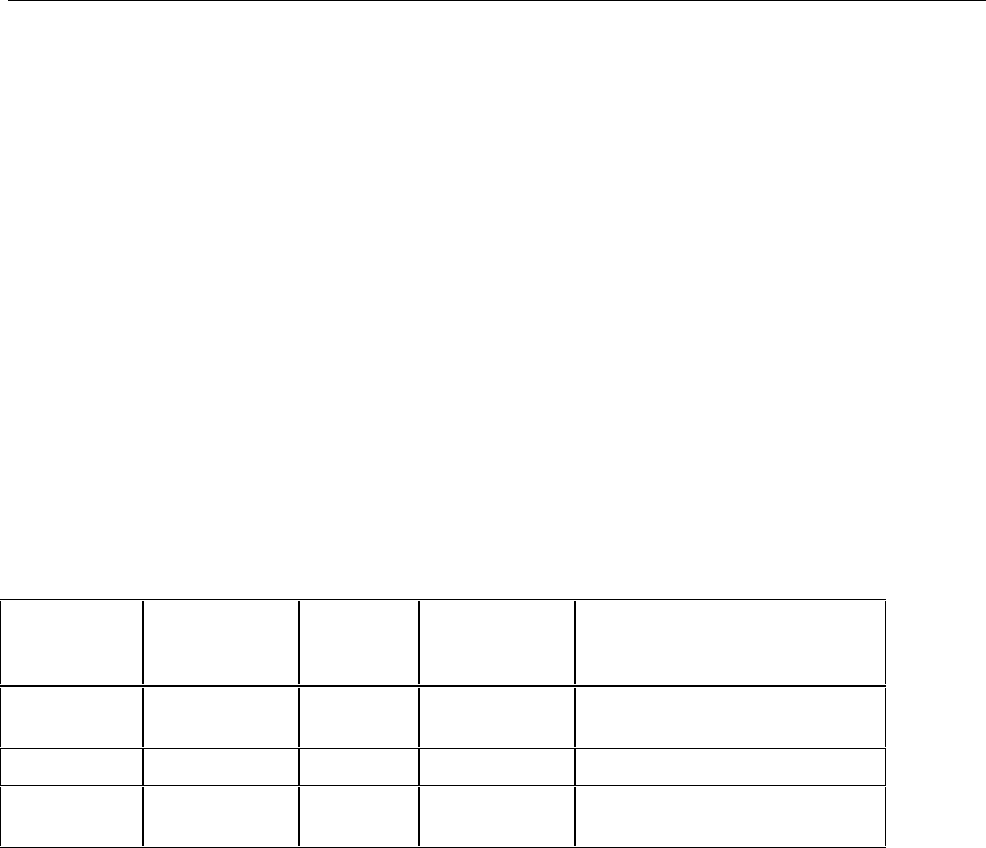
Table 3-1. Standards for Calibrating 5700A/5720A Series II
Fluke
Standard
Traceable
Quantity
Nominal
Value
Uncertainty
Limit
5700A/5720A Series II
Specifications susceptible to
Uncertainty Limit
732B Voltage 10V ±1.5 ppm
dc volts, ac volts,
dc current, ac current
742A-1 Resistance 1Ω ±10 ppm 1Ω, 1.9Ω
742A-10k Resistance 10 kΩ ±4 ppm
ac current, dc current 10Ω to
100 MΩ


















