3-4 Installation and Maintenance Volume
Octel 200/300 S.4.1 PB60019−01
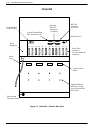
Figure 3-3 is a block diagram of the Octel 200/300 connected to the phone system where all incoming
lines are directed to it. Arrows denote hunting.
Figure 3-3 All Incoming Lines Directed to the Octel 200/300
PBX
Octel
200/300
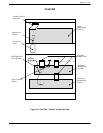
Figure 3-4 is a block diagram of the Octel 200/300 connected to a phone system that has incoming lines
split between the console and the Octel 200/300. Arrows denote hunting.
Figure 3-4 Incoming Calls Split Between Console and the
Octel 200/300
PBX
Octel
200/300
Acting as a Message Center
The Octel 200/300 can answer forwarded calls when the PBX does not provide the information needed to
support integration with the message server. The PBX may send only the digits associated with a
forwarded extension, using DTMF tones. The message server in that environment cannot detect that the
call was forwarded. To prevent the message server from acting on the received digits by trying to call the
extension again, ports are configured in CX mode. The Octel 200/300 does not attempt to call the
extension number but instead immediately goes to that extension’s mailbox, plays the appropriate prompt
or greeting, and if configured to do so, offers to take a message.
The attendant may also extend callers to a port to allow them to leave a voice message. This port is
configured as MX mode. It does not call the extension number entered but goes to that extension’s
mailbox and offers to take a message.