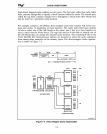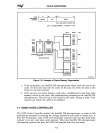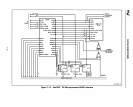
1386"
OX
CPU
CACHE SUBSYSTEMS
OTHER BUS
MASTER
_________
} NON·CACHEABLE
MEMORY
}
CACHE
CACHEABLE
~
231732i7·8
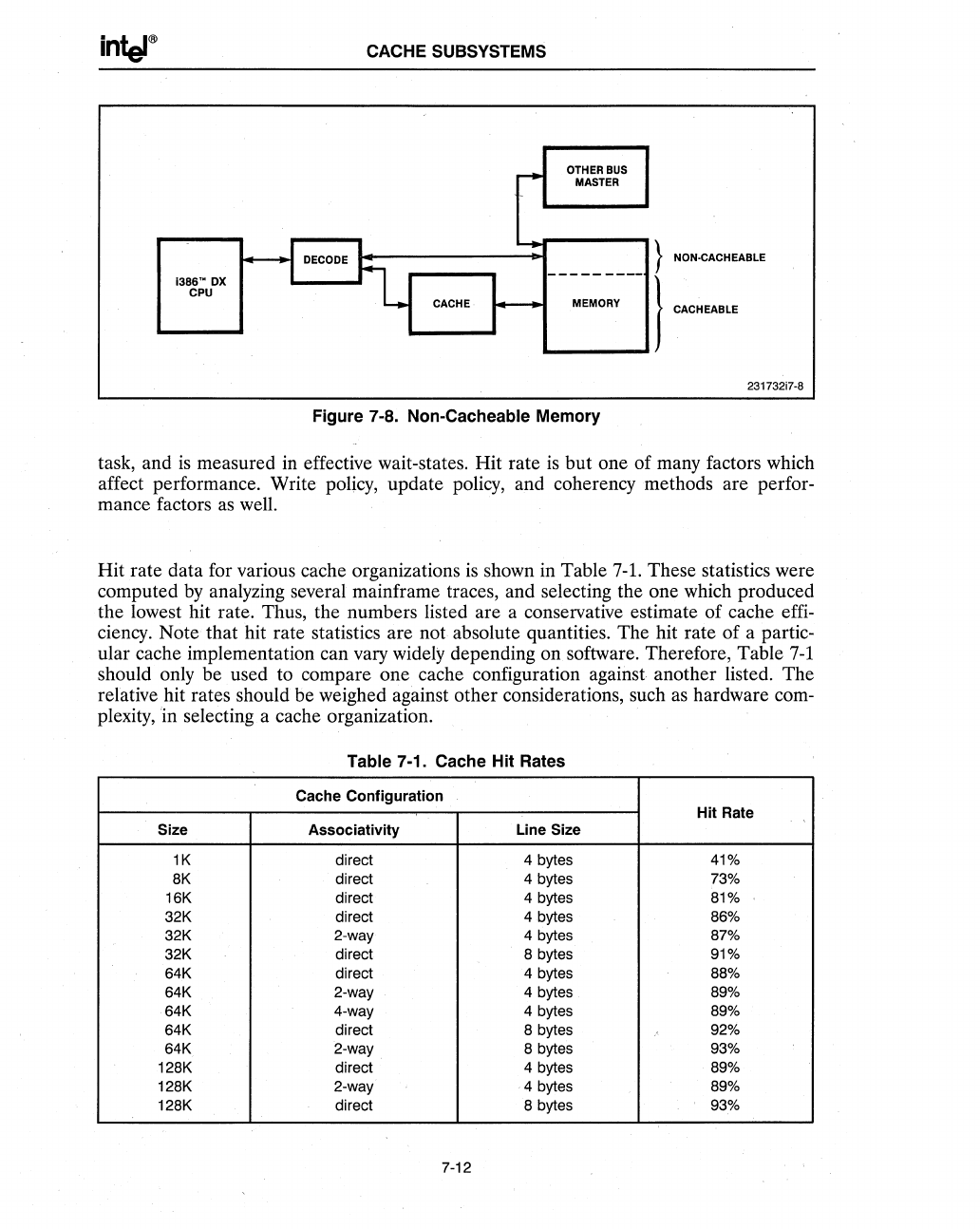
Figure 7-8. Non-Cacheable Memory
task, and
is
measured in effective wait-states. Hit rate
is
but one of many factors which
affect performance. Write policy, update policy, and coherency methods are
perfor-
mance factors
as
well.
Hit rate data for various cache organizations
is
shown in Table
7-1.
These statistics were
computed
by
analyzing several mainframe traces, and selecting the one which produced
the lowest hit rate. Thus, the numbers listed are a conservative estimate of cache
effi-
ciency. Note that hit rate statistics are
not
absolute quantities. The hit rate of a partic-
ular cache implementation can vary widely depending on software. Therefore, Table
7-1
should only be. used to compare one cache configuration against another listed. The
relative hit rates should be weighed against other considerations, such
as
hardware com-
plexity,
in
selecting a cache organization.
Table 7-1. Cache Hit Rates
Cache
Configuration
Hit
Rate
Size
Associativity
Line Size
1K
direct
4 bytes 41%
8K direct 4 bytes
73%
16K direct 4 bytes 81%
32K direct 4 bytes 86%
32K
2-way 4 bytes 87%
32K direct 8 bytes
91%
64K direct 4 bytes 88%
64K 2-way 4 bytes 89%
64K
4-way 4 bytes 89%
64K direct 8 bytes
.'.
92%
64K
2-way
8 bytes 93%
128K direct 4 bytes 89%
128K
2-way
4 bytes 89%
128K direct 8 bytes 93%
7-12