82289AEN#
MUl
TlBUS XACK#
(BUS
CONTROllER)
ENOCYC2
ADSO#
ClK
82288 ALE
MUL TIBUS I AND Intel386
OX
MICROPROCESSOR
--
ARDY
]
y--
J
Q
r-
K
r--
>
~
WS1
WS1
J
Q
K
85C220
WS2
J"">--=
......
ClK#
READY#
....
I--
PClK
MOEN
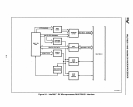
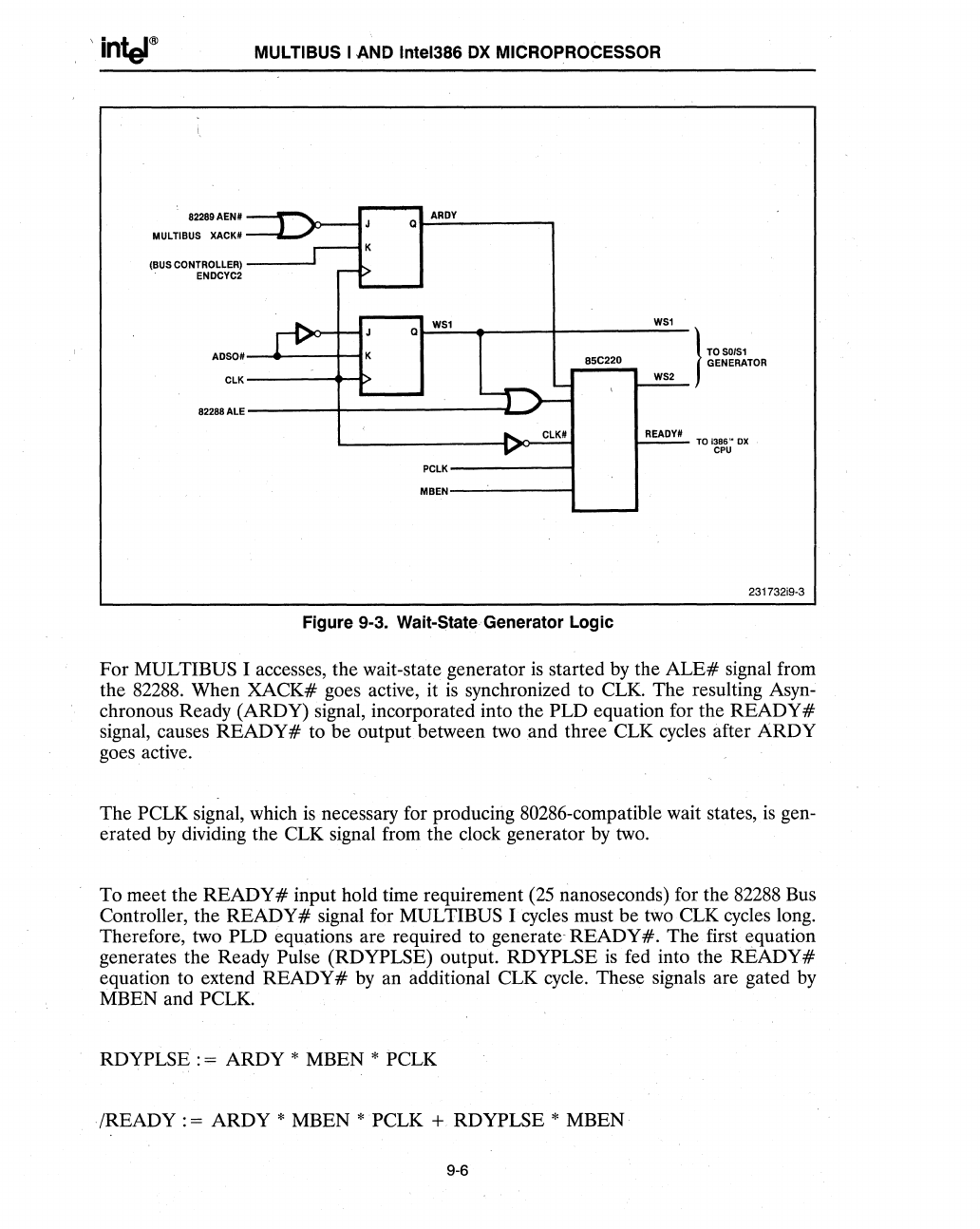
Figure 9-3. Wait-State Generator Logic
I
TOSO/S1
GENERATOR
TO
i386'·
OX
CPU
231732i9-3
For MULTIBUS I accesses, the wait-state generator
is
started
by
the
ALE#
signal from
the
82288.
When XACK# goes active, it
is
synchronized to CLK. The resulting Asyn-
chronous Ready (ARDY) signal, incorporated into the PLD equation for the READY #
signal, causes
READY#
to be output between
two
and three CLK cycles after
ARDY
goes active.
The
PCLK signal, which
is
necessary for producing 80286-compatible wait states,
is
gen-
erated
by
dividing the CLK signal from the clock generator
by
two.
To meet the
READY#
input hold time requirement
(25
nanoseconds) for the 82288 Bus
Controller, the
READY#
signal for MULTIBUS I cycles must be
two
CLK cycles long.
Therefore, two
PLD equations are required to generate
READY#.
The first equation
generates the Ready
Pulse (RDYPLSE) output. RDYPLSE
is
fed into the READY #
equation to extend READY #
by
an additional CLK cycle. These signals are gated
by
MBEN and PCLK.
RDYPLSE
: = ARDY * MBEN * PCLK
/READY : =
ARDY
* MBEN * PCLK + RDYPLSE * MBEN
9-6