PERFORMANCE CONSIDERATIONS
Consider a system in which a non-pipelined memory access requires one wait state and a
non-pipelined
I/O access requires four wait states. The bus control logic reads chip select
signals from the address decoder to determine whether one or four wait states are
required for the bus cycle. The bus control logic also determines whether the address has
been pipelined, because a pipelined cycle
requires one less wait state. The system
includes logic for generating a Bus Idle signal that indicates whether the bus cycle has
ended. The bus control logic can therefore detect that the address has been pipe lined if
the Address Status
(ADS#)
signal goes active while the Bus Idle signal
is
inactive.
Address pipelining
is
less effective for I/O devices requiring several wait states. The
larger the number of wait states required, the less significant the elimination of one wait
state through pipelining becomes. This fact coupled with the relative infrequency of
I/O
accesses means that address pipelining for I/O devices usually makes little difference to
system performance.
A third and less common approach to accommodating memory speed
is
reducing the
Intel386
DX
microprocessor operating frequency. Because a slower clock frequency
increases the bus cycle time, fewer wait states may be required for particular memory
devices.
At
the same time, however, system performance depends directly on
the'
Inte1386
DX
microprocessor clock frequency; execution time increases in direct propor-
tion to the increase in clock period (reduction in clock frequency).
The design and application determine whether frequency reduction makes sense.
In
some instances, a slight reduction in clock frequency reduces the wait-state requirement
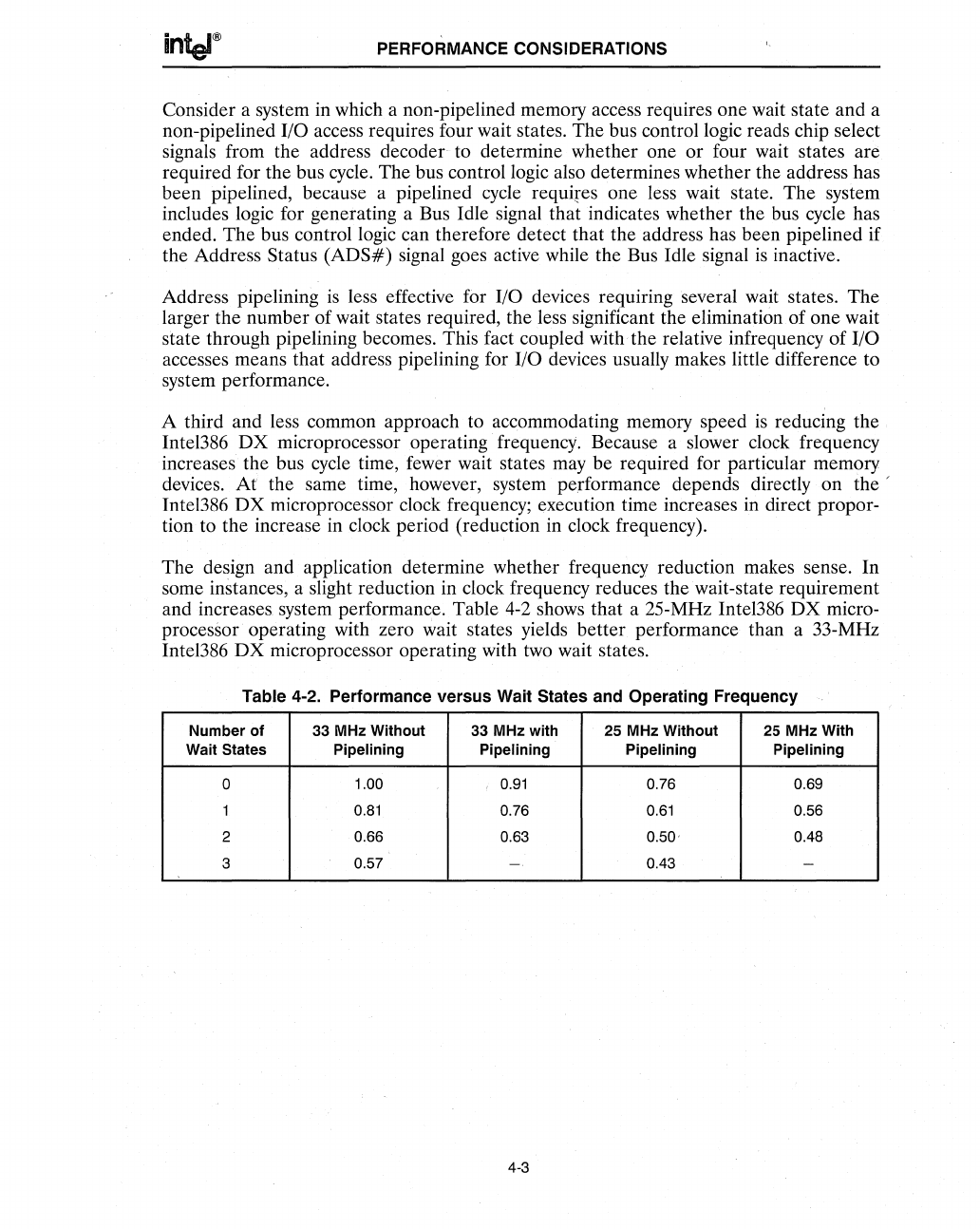
and increases system performance. Table
4-2
shows that a 25-MHz Inte1386
DX
micro-
processor operating with zero wait states yields better performance than a 33-MHz
Inte1386
DX
microprocessor operating with two wait states.
Table 4-2. Performance versus Wait States and Operating Frequency
Number of 33
MHz
Without 33
MHz
with 25
MHz
Without 25 MHz With
Wait States Pipelining Pipelining
Pipelining
Pipelining
0
1.00 0.91 0.76 0.69
1
0.81
0.76 0.61 0.56
2 0.66 0.63
0.50'
0.48
3
0.57
-,
0.43 -
4-3