CACHE SUBSYSTEMS
The
82385
resides on the Inte1386 DX microprocessor local bus and interfaces directly
to
the Intel386 DX microprocessor.
It
presents a 'functional
Inte1386
DX microprocessor
bus (called the
82385
local bus) for the system interface. This dual bus structure and the
82385's ability to
"snoop" the system interface allows the Inte1386 DX microprocessor to
run locally out of the cache while another bus master has control of the
82385
local bus.
7.7.1 Bus Structure with the 82385
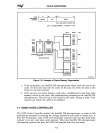
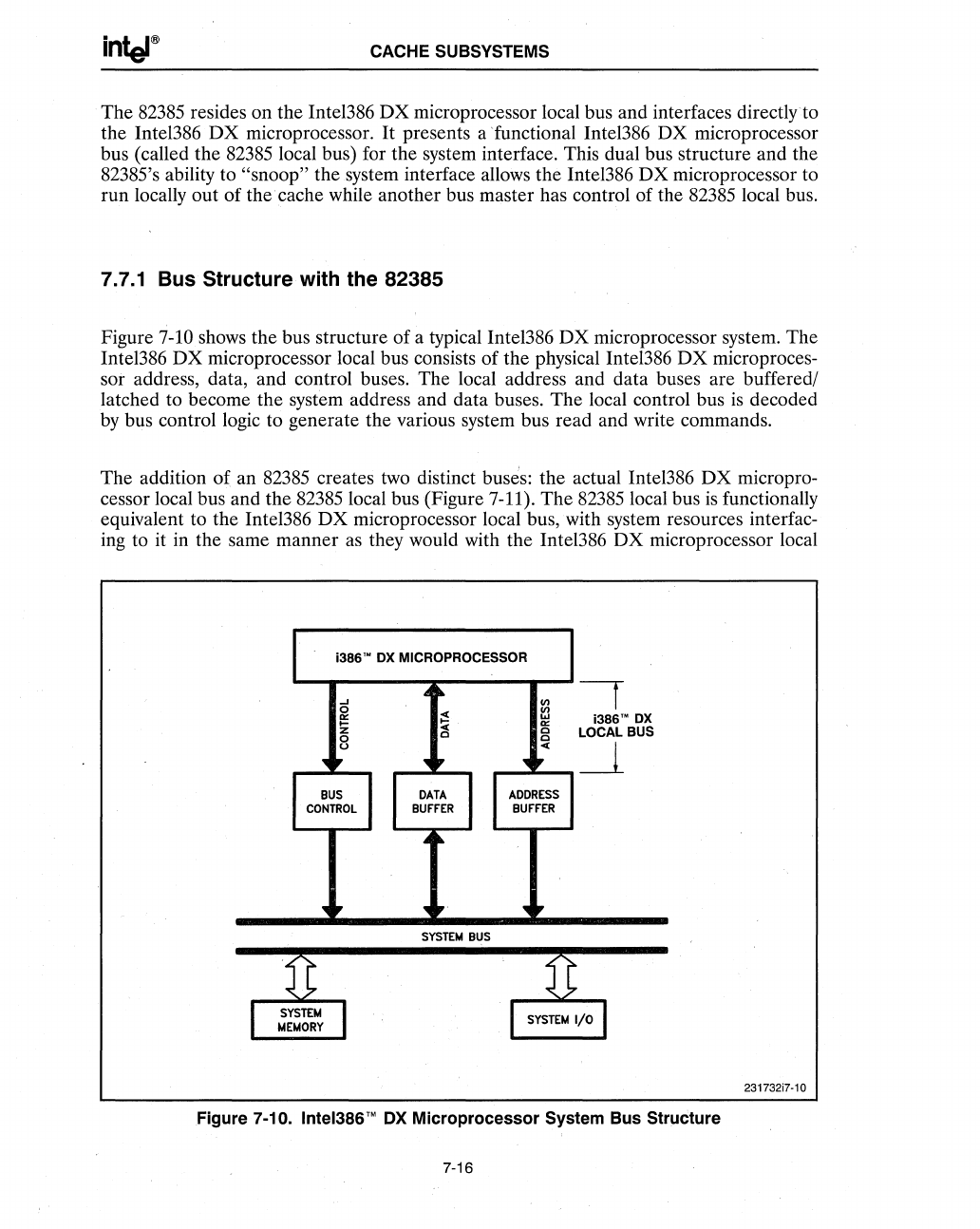
Figure
7-10
shows the bus structure of a typical Intel386
DX
microprocessor system. The
Intel386 DX microprocessor local bus consists of the physical Intel386
DX
microproces-
sor address, data, and control buses. The local address and data buses are buffered/
latched to become the system address and data buses. The local control bus
is
decoded
by
bus control logic to generate the various system bus read and write commands.
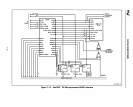
The addition
of an
82385
creates two distinct buses: the actual Intel386
DX
micropro-
cessor local bus and the
82385
local bus (Figure 7-11). The
82385
local bus
is
functionally
equivalent to the Inte1386
DX
microprocessor local bus, with system resources interfac-
ing to it in the same manner
as
they would with the Intel386 DX microprocessor local
i386'·
ox
MICROPROCESSOR
...
0
I!:
z
0
0
"II
,.
8US
CONTROL
"II
,.
SYSTEM
MEMORY
4
~
~
C§
~
r
DATA
BUFFER
~
~
~
r'
SYSTEM
BUS
(II
I
(II
...
i386'·
ox
'"
c
LOCAL BUS
c
«
~
"II
,.
ADDRESS
BUFFER
"II
,.
SYSTEM
I/O
I
Figure 7-10. Intel386™
OX
Microprocessor System Bus StrlJcture
7-16
231732i7-10