LOCAL BUS INTERFACE
IDLE
CYCLE
1
NON-PIPELINED
(WRITE)
CYCLE
2
NON-PIPELINED
(READ)
CYCLE
3
PIPELINED
(WRITE)
CYCLE
~
PIPELINED
(READ)
n
T1
T2
T1
T2
T2P
T1
P
T2P
T1
P
T21
CLK2
[
CLK
[
8EO#
- 8E3# [
A2-A31.
W/IO#.D/C#
W/R#
[
ADS#
[
NA# [
8516#
[
£¥~t:::£.~~M?'~~>C::l.~
READY#
[
C¥~c.!.~~~~-+~~~'"
IDLE
n
LOCK
# [
"'~~r'-......;;;;:;;:....:.....-r'--+-----r
'---:----r
'-.......;~---f\j~~
00-
031
[
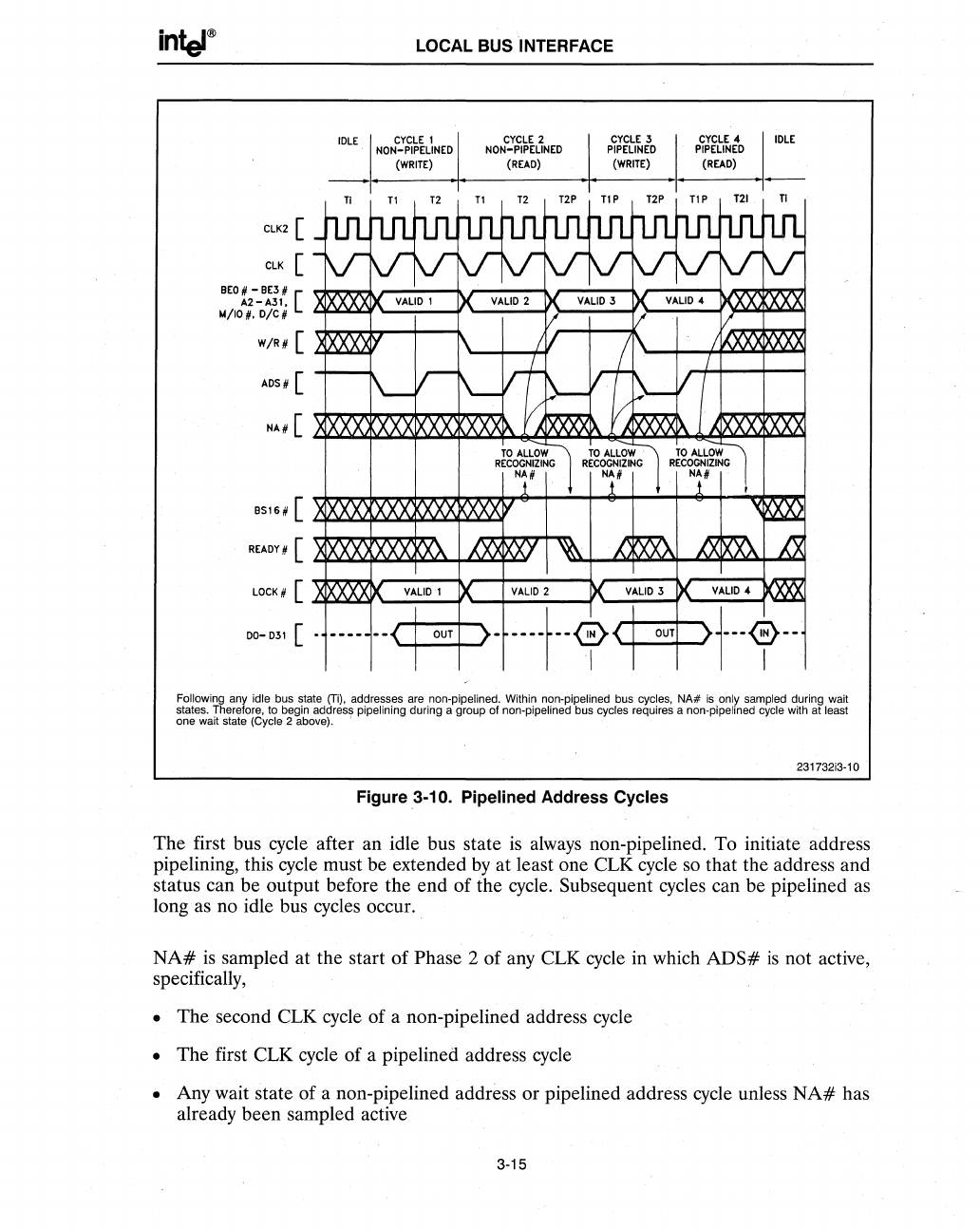
Following any idle bus state
(Ti),
addresses are non-pipelined. Within non-pipelined bus cycles,
NA#
is
only sampled during wait
states. Therefore, to begin address pipelining during a group of
non-pipelined bus cycles requires a non-plpelined cycle with at least
one wait state (Cycle 2 above). '
231732i3-10
Figure .3-10. Pipelined Address Cycles
The first bus
cycle
after an idle bus state
is
always
non-pipelined. To initiate address
pipelining, this
cycle
must be extended
by
at least one
eLK
cycle
so that the address and
status can be output before the end of the cycle. Subsequent cycles can be pipelined
as
long
as
no idle bus cycles occur.
NA#
is
sampled at the start of Phase 2 of any
eLK
cycle
in which
ADS#
is
not active,
specifically,
• The second
eLK
cycle
of a non-pipelined address
cycle
• The first
eLK
cycle of a pipelined address
cycle
• Any wait state of a non-pipelined address or pipelined address
cycle
unless
NA#
has
already been sampled active
3-15