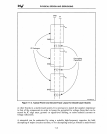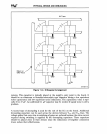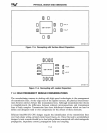
PHYSICAL DESIGN AND DEBUGGING
11.4.1.1 TRANSMISSION LINE TYPES
Although many different types of transmission lines (conductors) exist, those most com-
monly used on the printed circuit boards are micro strip lines, strip lines, printed circuit
traces, side-by-side conductors and flat conductors.
11.4.1.1.1 Micro Strip Lines
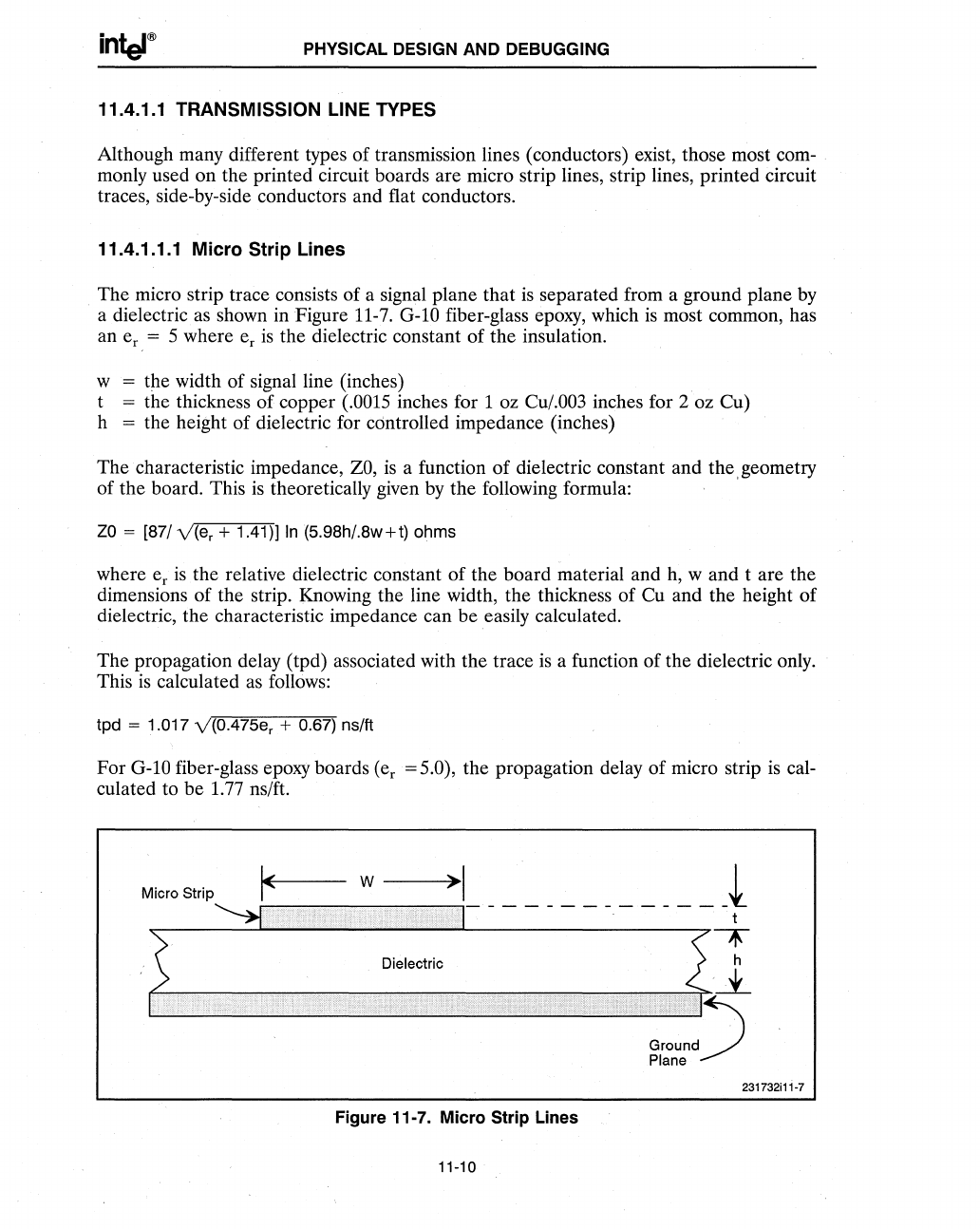
The micro strip trace consists of a signal plane that
is
separated from a ground plane
by
a dielectric
as
shown in Figure
11-7.
G-IO
fiber-glass epoxy, which
is
most common, has
an e
r
= 5 where e
r
is
the dielectric constant of the insulation.
w
= the width of signal line (inches) .
t = the thickness of copper (.0015 inches for 1
oz
CU/.003
inches for 2 oz Cu)
h
= the height of dielectric for controlled impedance (inches)
The characteristic impedance,
ZO,
is
a function of dielectric constant and the, geometry
of the board. This
is
theoretically given
by
the following formula:
ZO
=
[87/v'(e
r
+ 1.41)]
In
(5.98h/.8w+t) ohms
where e
r
is
the relative dielectric constant of the board material and h,
wand
t are the
dimensions of the strip. Knowing the line width, the thickness of Cu and the height
of
dielectric, the characteristic impedance can be easily calculated.
The propagation delay (tpd) associated with the trace
is
a function of the dielectric only.
This
is
calculated
as
follows:
tpd = 1.017 v'(0.475e
r
+ 0.67) ns/ft
For G-lO fiber-glass epoxy boards
(e
r
= 5.0), the propagation delay
of
micro strip
is
cal-
culated to be
1.77
ns/ft.
Micro Strip
w
------+>1
_____________
~
231732ill-7
Figure 11-7. Micro Strip Lines
11-10